2567. Code
the Tree
A tree (i.e. a
connected graph without cycles) with vertices numbered by the integers 1, 2,
..., n is given. The
"Prufer" code of such a tree is built as follows: the leaf (a vertex
that is incident to only one edge) with the minimal number is taken. This leaf,
together with its incident edge is removed from the graph, while the number of
the vertex that was adjacent to the leaf is written down. In the obtained
graph, this procedure is repeated, until there is only one vertex left (which,
by the way, always has number n). The
written down sequence of n – 1
numbers is called the Prufer code of the tree.
Your task is, given
a tree, to compute its Prufer code. The tree is denoted by a word of the
language specified by the following grammar:
T ::= "("
N S ")"
S ::= " "
T S
| empty
N ::= number
That is, trees have
parentheses around them, and a number denoting the identifier of the root
vertex, followed by arbitrarily many (maybe none) subtrees separated by a
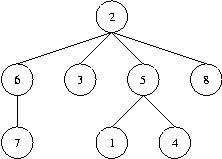
single space character. As an example, take a look at the tree in the figure
below which is denoted in the first line of the sample input. To generate
further sample input, you may use your solution to Problem 2568.
Note that,
according to the definition given above, the root of a tree may be a leaf as
well. It is only for the ease of denotation that we designate some vertex to be
the root. Usually, what we are dealing here with is called an "unrooted
tree".
Input. The input contains several test cases. Each test case
specifies a tree as described above on one line of the input file. Input is
terminated by EOF. You may assume that 1 ≤ n ≤ 50.
Output. For each test case generate a single line containing the
Prufer code of the specified tree. Separate numbers by a single space. Do not
print any spaces at the end of the line.
Sample Input
(2 (6 (7)) (3) (5 (1) (4)) (8))
(1 (2 (3)))
(6 (1 (4)) (2 (3) (5)))
Sample Output
5 2 5 2 6 2 8
2 3
2 1 6 2 6
РЕШЕНИЕ
коды Прюфера
Анализ алгоритма
По заданному дереву
необходимо составить код Прюфера. Только следует вывести код длины n – 1.
Определение.
Кодом Прюфера длины n – 2 называется последовательность из чисел от 1 до
n с повторениями.
Теорема.
Существует взаимно однозначное соответствие между остовными деревьями для графа
из n вершин и кодами Прюфера длины n – 2. По каждому дереву с n
вершинами можно построить код Прюфера длины n – 2 и наоборот.
Вход: дерево
с n вершинами.
Выход: код
Прюфера длины n – 2.
Повторить n – 2 раза
Выбрать вершину v – лист дерева с наименьшим
номером;
Добавить в код Прюфера номер вершины, смежной с v;
Удалить вершину v с инцидентным ей ребром из
дерева;
Реализация алгоритма
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX 100000
char s[MAX];
int g[51][51], deg[51];
int i, j, t, n;
int GetGraph(void)
{
int v;
scanf("%d%*[ ]",&v);
if (v > n) n = v;
char ch;
scanf("%c%*[ ]",&ch);
while(ch == '(')
{
int to = GetGraph();
g[v][to] = g[to][v]
= 1;
scanf("%c%*[ ]",&ch);
}
return v;
}
int main(void)
{
char ch;
while(scanf("%c",&ch)
== 1)
{
memset(g,0,sizeof(g));
scanf("(",&ch);
n = 0; GetGraph();
scanf("\n");
memset(deg,0,sizeof(deg));
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (g[i][j]) deg[i]++;
for(t = 1; t <= n; t++)
{
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (deg[i] == 1)
{
deg[i]--;
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (g[i][j])
{
g[i][j]
= g[j][i] = 0;
deg[j]--;
if (t !=
1) printf(" ");
printf("%d",j);
goto fin;
}
}
fin:;
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}