3204. Ikki's Story I - Road Reconstruction
Ikki is the king of a small country – Phoenix, Phoenix
is so small that there is only one city that is responsible for the production
of daily goods, and uses the road network to transport the goods to the capital.
Ikki finds that the biggest problem in the country is that transportation speed
is too slow.
Since Ikki was an ACM/ICPC contestant before, he
realized that this, indeed, is a maximum flow problem. He coded a maximum flow
program and found the answer. Not satisfied with the current status of the
transportation speed, he wants to increase the transportation ability of the
nation. The method is relatively simple, Ikki will reconstruct some roads in
this transportation network, to make those roads afford higher capacity in
transportation. But unfortunately, the country of Phoenix is not so rich in GDP
that there is only enough money to rebuild one road. Ikki wants to find such
roads that if reconstructed, the total capacity of transportation will
increase.
He thought this problem for a loooong time but cannot
get it. So he gave this problem to frkstyc, who put it in this POJ Monthly
contest for you to solve. Can you solve it for Ikki?
Input. The input contains exactly one test case.
The first line of the test
case contains two integers n, m (n
≤ 500, m ≤ 5,000) which
represents the number of cities and roads in the country, Phoenix,
respectively.
m lines follow, each line contains three integers a, b,
c, which means that there is a road
from city a to city b with a transportation capacity of c (0 ≤ a, b < n, c
≤ 100). All the roads are directed.
Cities are numbered from 0
to n − 1, the city which can
product goods is numbered 0, and the capital is numbered n − 1.
Output. You should output one line consisting of only one
integer k, denoting that there are k roads, reconstructing each of which
will increase the network transportation capacity.
Sample Input
2 1
0 1 1
Sample
Output
1
РЕШЕНИЕ
графы – максимальный поток
Анализ алгоритма
Ищем максимальный поток в
сети (например Диницем). Строим остаточную сеть. В остаточной сети запустим
поиск в глубину со стартовой нулевой вершины по ребрам с ненулевой пропускной
способностью, отметив все достижимые вершины например в used[i][0]. Затем в остаточной сети запустим обратный
поиск в глубину с конечной (n – 1)-ой
вершины по ребрам с ненулевой прямой пропускной способностью (двигаться по
ребру (u, v) от вершины v к u разрешено, если только Cap[u][v]
> 0), отметив все достижимые вершины например в used[i][1].
Остается
подсчитать количество таких ребер (u,
v), для которых истинно used[u][0] и used[v[1], а также которые имеют в остаточной сети нулевую пропускную
способность.
Пример
Слева изображена исходная
сеть. Справа – остаточная. Максимальный поток равен 16.
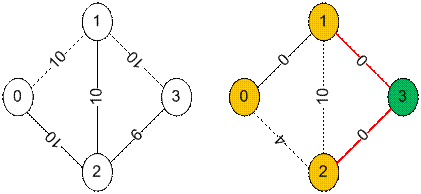
Поиск в глубину из 0 по
остаточной сети пройдет по вершинам 0, 2, 1.
Поиск в глубину из 3 по
остаточной сети пройдет по вершинам 3.
Ребрами нулевой пропускной
способности, соединяющими вершины из разных множеств, будут (1, 3) и (2, 3).
Реализация алгоритма
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#define MAX
510
#define INF
0x3F3F3F3F
using namespace std;
long long Cap[MAX][MAX], CapStart[MAX][MAX];
int
ptr[MAX], d[MAX];
int a, b,
c, n, Edges;
int i, j,
res;
long long MaxFlow;
int
used[MAX][2];
long long min(long long i, long long j)
{
return (i
< j) ? i : j;
}
long long bfs(int s)
{
int q[MAX];
int qh = 0,
qt = 0;
q[qt++] = s;
memset (d, -1, sizeof(d));
d[s] = 0;
while (qh
< qt)
{
int v =
q[qh++];
for (int to = 0; to < n; to++)
if
((d[to] == -1) && Cap[v][to])
{
q[qt++] = to;
d[to] = d[v] + 1;
}
}
return d[n-1]
!= -1;
}
long long dfs(int v, long long flow)
{
if
(!flow) return
0;
if (v == n -
1) return
flow;
for (int &to = ptr[v]; to < n; to++)
{
if (d[to]
!= d[v] + 1) continue;
int pushed
= dfs (to, min (flow, Cap[v][to]));
if (pushed)
{
Cap[v][to] -= pushed;
Cap[to][v] += pushed;
return
pushed;
}
}
return 0;
}
long long Dinic(int s)
{
long long flow = 0;
for (;;)
{
if
(!bfs(s)) break;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) ptr[i] = 0;
while (long long pushed =
dfs (s, INF))
flow += pushed;
}
return flow;
}
void
goForward(int v)
{
int i;
used[v][0] = 1;
for(i = 0; i
< n; i++)
if
(!used[i][0] && (Cap[v][i] > 0)) goForward(i);
}
void
goBack(int v)
{
int i;
used[v][1] = 1;
for(i = 0; i
< n; i++)
if
(!used[i][1] && (Cap[i][v] > 0)) goBack(i);
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&n,&Edges);
memset(Cap,0,sizeof(Cap));
while
(Edges--)
scanf("%d
%d %d",&a,&b,&c), Cap[a][b] += c;
memcpy(CapStart,Cap,sizeof(Cap));
MaxFlow = Dinic(0);
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
goForward(0);
goBack(n-1);
res = 0;
for(i = 0; i
< n; i++)
for(j = 0; j
< n; j++)
if ((CapStart[i][j] > 0) && (Cap[i][j] ==
0) && used[i][0] && used[j][1])
res++;
printf("%d\n",res);
return 0;
}