1466. Girls and Boys
In the second year of the university somebody started
a study on the romantic relations between the students. The relation
"romantically involved" is defined between one girl and one boy. For
the study reasons it is necessary to find out the maximum set satisfying the
condition: there are no two students in the set who have been
"romantically involved". The result of the program is the number of
students in such a set.
Input. The input contains several data sets in text format.
Each data set represents one set of subjects of the study, with the following
description:
the number of students
the description of each student, in the following format
student_identifier:(number_of_romantic_relations)
student_identifier1 student_identifier2 student_identifier3 ...
or
student_identifier:(0)
The student_identifier is
an integer number between 0 and n – 1
(n ≤ 500), for n subjects.
Output. For each given data set, the program should write to
standard output a line containing the result.
Sample Input
7
0: (3) 4 5
6
1: (2) 4 6
2: (0)
3: (0)
4: (2) 0 1
5: (1) 0
6: (2) 0 1
3
0: (2) 1 2
1: (1) 0
2: (1) 0
Sample Output
5
2
РЕШЕНИЕ
графы – максимальное паросочетание
Анализ алгоритма
Всего имеется n студентов – мальчиков и
девочек. Нам не известно, какие номера студентов являются мальчиками, а какие
девочками. Ребра проводятся только между студентами разного пола. Следовательно
романтический граф содержит n вершин
и является двудольным.
В задаче следует найти
размер максимального независимого множества. Оно равно количеству вершин в
двудольном графе минус размер минимального вершинного покрытия. Вычитаемое по
теореме Кенига равно максимальному паросочетанию.
Построим двудольный граф, в
каждой доле по n вершин. Проведем
ребра как указано во входных данных. Пусть в графе имеется ребро (a, b).
Тогда в нем будет присутствовать и ребро (b,
a). Пусть размер его максимального
паросочетания равен flow. Тогда
размер максимального независимого множества исходного графа равен n – flow
/ 2.
Пример
Рассмотрим первый тест.
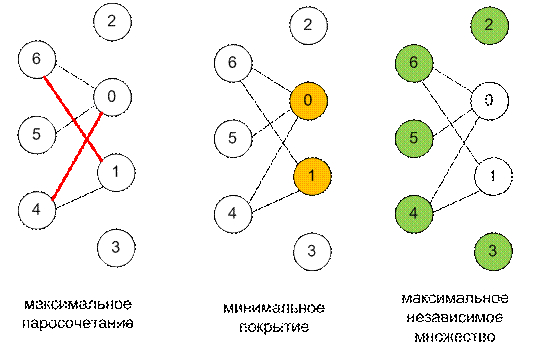
Размер максимального
независимого множества равен 5.
Реализация алгоритма
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int> > g;
vector<int> used, mt, par;
int i, n,
id, k, v, flow;
int dfs(int v)
{
if (used[v]) return 0;
used[v] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < g[v].size(); i++)
{
int to =
g[v][i];
if (mt[to]
== -1 || dfs(mt[to]))
{
mt[to] = v;
par[v] = to;
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
void
AugmentingPath(void)
{
int i, run;
mt.assign (n+1, -1);
par.assign (n+1, -1);
for (run = 1;
run; )
{
run = 0;
used.assign(n, 0);
for (i = 0;
i < n; i++)
if
((par[i] == -1) && dfs(i)) run = 1;
}
}
int main(void)
{
while(scanf("%d",&n) == 1)
{
g.assign(n,vector<int>());
for(i = 0;
i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d:
",&id);
scanf("(%d)",&k);
while(k--)
{
scanf("%d",&v);
g[id].push_back(v);
}
}
AugmentingPath();
for (flow =
0, i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (mt[i]
!= -1) flow++;
printf("%d\n",n
- flow/2);
}
return 0;
}