1847. Tram
Tram network in Zagreb consists of a
number of intersections and rails connecting some of them. In every
intersection there is a switch pointing to the one of the rails going out of
the intersection. When the tram enters the intersection it can leave only in
the direction the switch is pointing. If the driver wants to go some other way,
he/she has to manually change the switch.
When a driver has do drive from
intersection a to the intersection b he/she tries to choose the route that
will minimize the number of times he/she will have to change the switches
manually.
Write a program that will calculate
the minimal number of switch changes necessary to travel from intersection a to intersection b.
Input. The first
line of contains integers n, a and b, separated by a single blank character, 2 ≤ n ≤ 100, 1 ≤ a, b
≤ n, n is the number of intersections in the network, and intersections
are numbered from 1 to n.
Each of
the following n lines contain a
sequence of integers separated by a single blank character. First number in the
i-th line, ki (0 ≤ ki
≤ n – 1), represents the number
of rails going out of the i-th
intersection. Next ki
numbers represents the intersections directly connected to the i-th intersection.Switch in the i-th intersection is initially pointing
in the direction of the first intersection listed.
Output. The first
and only line of the output should contain the target minimal number. If there
is no route from A to B the line should contain the integer "-1".
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
3 2 1 2 2 3 2 3 1 2 1 2 |
0 |
РЕШЕНИЕ
графы - Дейкстра
Анализ алгоритма
1. Алгоритм Дейкстры. Рассмотрим
ребра графа, соответствующие направлениям, на которые указывают стрелки.
Установим их веса равными 0. Веса остальных ребер (возможных путей движения
трамвая) установим равными 1.
Кратчайший
путь из a в b, найденный алгоритмом Дейкстры, будет равен минимальному числу
переключений стрелок, достаточных для
проезда трамвая из a в b.
2. Поиск в ширину 0-1. Построим граф, в котором вершинами будут перекрестки, а ребрами –
всевозможные трамвайные пути. Если на перекрестке x переключатель стоит по направлению к перекрестку y, то положим вес ребра (x, y)
равным 0. Если от x можно изменить
состояние переключателя к y, то вес
ребра (x, y) положим равным 1.
Таким образом при движении от
перекрестка a к перекрестку b мы будем минимизировать не длину пути,
а количество переключений. Получили 0-1 граф. Воспользуемся поиском в ширину с
релаксацией ребер:
·
если
релаксирует ребро (x, y) весом 1, то кладем y в конец очереди.
·
если
релаксирует ребро (x, y) весом 0, то кладем y в начало очереди.
Пример
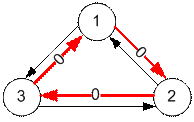
Ребра с весом 0 указывают на
начальное состояние направлений переключателей.
Реализация алгоритма - Дейкстра
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#define MAX
110
#define INF
0x3F3F3F3F
using namespace std;
int i, j,
w, v, k, to, cost, n, m, a, b;
int
used[MAX], dist[MAX];
vector<vector<pair<int, int> >
> g;
void
Relax(int v, int
to, int cost)
{
if (dist[to]
> dist[v] + cost)
dist[to] = dist[v] + cost;
}
int Find_Min(void)
{
int i, v =
-1, min = INF;
for(i = 1; i
<= n; i++)
if
(!used[i] && (dist[i] < min)) min = dist[i], v = i;
return v;
}
void
Dijkstra(int start, int
finish)
{
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
memset(dist,0x3F,sizeof(dist));
dist[start] = 0;
for(i = 1; i
< n; i++)
{
v = Find_Min();
used[v] = 1;
if (v ==
-1) break;
for(j = 0;
j < g[v].size(); j++)
{
to = g[v][j].first;
cost = g[v][j].second;
if
(!used[to]) Relax(v,to,cost);
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d %d
%d",&n,&a,&b);
g.resize(n+1);
for(i = 1; i
<= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&k);
for(j = 0;
j < k; j++)
{
scanf("%d",&to);
w = (j == 0) ? 0 : 1;
g[i].push_back(make_pair(to,w));
}
}
Dijkstra(a,b);
if (dist[b]
== INF)
printf("-1\n");
else
printf("%d\n",dist[b]);
return 0;
}
Реализация алгоритма – поиск в ширину 0-1
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#define MAX 110
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
using namespace
std;
int i, j, w, v, k, to, cost, n, m, a,
b;
int dist[MAX];
vector<vector<pair<int,
int> > > g;
void bfs(int
start)
{
memset(dist,0x3F,sizeof(dist));
dist[start] = 0;
deque<int> q;
q.push_back(start);
while(!q.empty())
{
int v = q.front(); q.pop_front();
for(int i = 0; i <
g[v].size(); i++)
{
int to = g[v][i].first;
int w = g[v][i].second;
if ((w == 1) && (dist[to] > dist[v] + 1))
{
q.push_back(to);
dist[to] = dist[v]
+ 1;
}
if ((w == 0) && (dist[to] > dist[v]))
{
q.push_front(to);
dist[to] =
dist[v];
}
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&a,&b);
g.resize(n+1);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&k);
for(j = 0; j < k; j++)
{
scanf("%d",&to);
w = (j == 0) ? 0
: 1;
g[i].push_back(make_pair(to,w));
}
}
bfs(a);
if (dist[b] == INF)
printf("-1\n");
else
printf("%d\n",dist[b]);
return 0;
}