4206. Fast
Maximum Matching
FJ
has n (1 ≤ n ≤ 50,000) cows and m
(1 ≤ m ≤ 50,000) bulls.
Given a list of p (1 ≤ p ≤ 150,000) potential matches
between a cow and a bull, compute the greatest number of pairs that can be
matched. Of course, a cow can be matched to at most one bull, and vice versa.
Input. The first line contains three
integers n, m and p. Each of the next
p lines contains two integers a (1 ≤ a ≤ n) and b (1 ≤ b ≤ m), denoting
that cow a can be matched with bull b.
Output. Print a single integer that is the
maximum number of pairs that can be obtained.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
5 4 6 5 2 1 2 4 3 3 1 2 2 4 4 |
3 |
РЕШЕНИЕ
графы – максимальное
паросочетание
Анализ
алгоритма
Для нахождения максимального паросочетания реализуем алгоритм дополняющего пути.
Пример
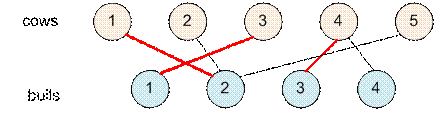
Реализация
алгоритма
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace
std;
vector<vector<int>
> g;
vector<int> used, mt,
par;
int i, j, ptr;
int n, m, k, a, b, flow;
int dfs(int
v)
{
if (used[v]) return
0;
used[v] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i
< g[v].size(); i++)
{
int to = g[v][i];
if (mt[to] == -1 || dfs(mt[to]))
{
mt[to] = v;
par[v] = 1;
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
void AugmentingPath(void)
{
int i, run;
mt.assign (m+1, -1);
par.assign (n+1, -1);
for (run = 1; run; )
{
run = 0;
used.assign(n+1, 0);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if ((par[i] == -1) && dfs(i)) run = 1;
}
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&m,&k);
g.resize(n+1);
for(i = 0; i
< k; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
g[a].push_back(b);
}
AugmentingPath();
for (flow = 0, i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if (mt[i] != -1) flow++;
printf("%d\n",flow);
return 0;
}