709. The
day of the competitors
The International
Olympiad in Informatics is coming and the leaders of the Vietnamese Team have
to choose the best contestants all over the country. Fortunately, the leaders
could choose the members of the team among n
very good contestants, numbered from 1 to n
(3 ≤ n ≤ 100000). In
order to select the best contestants the leaders organized three competitions.
Each of the n contestants took part
in all three competitions and there were no two contestants with equal results
on any of the competitions. We say that contestant А is better than another
contestant В when А is ranked before В in all of the competitions. A contestant
A is said to be excellent if no other contestant is better than A. The leaders
of the Vietnamese Team would like to know the number of excellent contestants.
Input.
First line contains an integer t (1 ≤ t ≤ 10
), equal to the number of testcases. Then descriptions of t testcases follow. First line of description contains the number
of competitors n . Each of the next n lines describes one competitor and
contains integer numbers ai,
bi, ci (1 ≤ ai,
bi, ci ≤ n )
separated by spaces, the order of i-th
competitor's ranking in the first competition , the second competition and the
third competition.
Output.
For each test case in the input your program should output
the number of excellent contestants in one line.
Sample Input
1
3
1 2 3
2 3 1
3 1 2
Sample Output
3
РЕШЕНИЕ
дерево отрезков
Анализ алгоритма
Каждый участник представлен
тройкой (a, b, c). Отсортируем тройки по первой компоненте (по условию все значения ai, bi, ci между собой различны).
Рассмотрим на плоскости n точек с координатами (bi, ci). Если относительно точки (bi, ci) не существует такой точки (bj, cj), что j < i и которая находится
одновременно левее и ниже, то она является превосходной.
Рассмотрим массив a[1; n], каждый элемент которого изначально равен бесконечности. Построим по нему дерево отрезков,
поддерживающего операцию минимума. Рассмотрим пары (bi, ci) в порядке возрастания им соответствующих ai. Найдем минимум на отрезке
[1; bi]. Если он больше ci, то в квадранте левее и ниже от (bi, ci) не лежит ни одна из уже
рассмотренных точек. Следовательно текущая тройка превосходная. Далее установим
a[bi] = ci и перейдем к рассмотрению
следующей точки.
Пример
Рассмотрим следующий тест:
1
5
1 1 4
2 5 2
3 3 5
4 2 1
5 4 3
Тройки для удобства уже
отсортированы по первой компоненте. Разместим на плоскости пары (bi, ci):
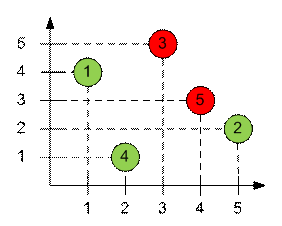
Зеленым цветом отмечены
превосходные тройки.
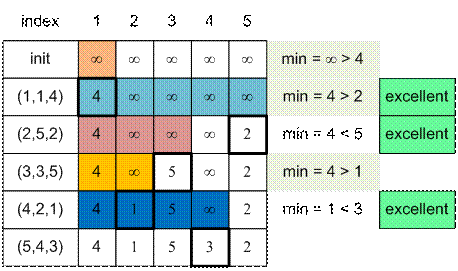
Реализация алгоритма
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#define MAX 100010
#define INF 2000000000
using namespace
std;
int i, n, tests, Result;
struct Strength
{
int a, b, c;
} Fight[MAX];
int SegmentTree[4*MAX];
int cmp(Strength x, Strength y)
{
return x.a < y.a;
}
void BuildTree(int
Vertex, int LeftPos, int
RightPos)
{
if (LeftPos == RightPos) SegmentTree[Vertex] = INF;
else
{
int Middle = (LeftPos + RightPos) / 2;
BuildTree(2*Vertex,
LeftPos, Middle);
BuildTree(2*Vertex+1, Middle+1, RightPos);
}
SegmentTree[Vertex] =
INF;
}
int GetMin(int
Vertex, int LeftPos, int
RightPos, int Left, int
Right)
{
if (Left > Right) return
INF;
if ((Left == LeftPos) && (Right == RightPos))
return SegmentTree[Vertex];
int Middle = (LeftPos + RightPos) / 2;
return min(GetMin(2*Vertex, LeftPos, Middle, Left,
min(Right,Middle)),
GetMin(2*Vertex+1, Middle+1, RightPos, max(Left,Middle+1),Right));
}
void update(int
Vertex, int LeftPos, int
RightPos, int Position,
int NewValue)
{
if (LeftPos == RightPos) SegmentTree[Vertex] =
NewValue;
else
{
int Middle = (LeftPos + RightPos) / 2;
if (Position <= Middle)
update(2*Vertex,
LeftPos, Middle, Position, NewValue);
else update(2*Vertex+1, Middle+1, RightPos, Position,
NewValue);
SegmentTree[Vertex]
= min(SegmentTree[2*Vertex],SegmentTree[2*Vertex+1]);
}
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&tests);
while(tests--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d %d %d",&Fight[i].a,
&Fight[i].b, &Fight[i].c);
// (a1, bi, ci) sort by the first component
// the less value - the winner
sort(Fight,Fight+n,cmp);
BuildTree(1,1,n);
// consider n Points (bi, ci) on the plane
// if no points from (bi,ci) to the left and to the bottom
// does
not exist, the point (bi,ci) is excellent
for(Result = i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int c = GetMin(1,1,n,1,Fight[i].b);
if (c > Fight[i].c)
{
Result++;
update(1,1,n,Fight[i].b,Fight[i].c);
}
}
printf("%d\n",Result);
}
return 0;
}