60. Area of a polygon
The coordinates of n consecutive points of polygon are
given. Find the area of the polygon.
Input. The number of polygon
vertices n is given in the first
line. In next n (3
≤ n ≤ 50000) lines the integer
coordinates of consecutive vertices xi, yi (-1000 ≤ xi,
yi ≤ 1000) are given.
Output. Print the area of the
polygon with 3 decimal digits.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
3 0 0 0 2 2 0 |
2.000 |
SOLUTION
geometry
Algorithm analysis
Let À1(x1, y1), À2(x2,
y2), …, Àn(xn,
yn) be the coordinates of the vertices of
a simple (without self-intersection) polygon, given in the order of traversing
it clockwise or counterclockwise. Then its area is calculated using the
trapezoidal formula:
S = ![]()
where Àn+1(xn+1, yn+1) = À1(x1, y1). The value of the sum should be taken modulo, since
it can be either positive or negative, depending on the direction of traversing
the polygon.
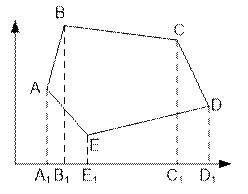
The area of the
trapezoid is positive for xi+1 > xi and negative for xi > xi+1.
The area of the polygon ABCDE equals to
![]() +
+ ![]() +
+ ![]() –
– ![]() –
– ![]()
The area of a polygon can be found
according to Surveyor
formula:
S = 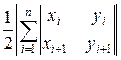 =
= 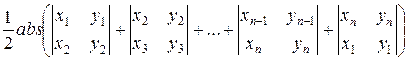
Let Î(0, 0) be the center of coordinates. Then
the area of the polygon is equal to the sum of the areas of triangles OA1A2, OA2A3, OA3A4, … , OAnA1. If the
triangle is oriented counterclockwise, then its area is positive. If against,
then it is negative. The area of the triangle OAiA i+1 is
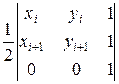 =
= 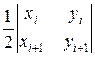
Algorithm realization
The coordinates of points store in
the vectors x and y. The coordinates of the i-th point store in (x[i], y[i]).
#define MAX 1002
int x[MAX], y[MAX];
The function findArea computes the area of a
polygon using the trapezoidal formula.
double findArea(int
*x, int *y)
{
double s = 0;
x[n] = x[0]; y[n] = y[0];
for(int i = 0; i <
n; i++)
s += (y[i+1] +
y[i]) * (x[i+1] - x[i]) / 2.0;
return (s < 0) ?
-s : s;
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d %d",&x[i],&y[i]);
Compute
and print the area of a polygon.
printf("%.3lf\n",findArea(x,y));
Algorithm realization – Surveyor formula
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
double
findArea(vector<int> &x, vector<int> &y)
{
double s;
int i;
x.push_back(x[0]); y.push_back(y[0]);
for(s = i =
0; i < x.size() - 1; i++)
s += y[i+1] * x[i] - y[i] * x[i+1];
return
fabs(s) / 2.0;
}
vector<int> x, y;
int i, n,
a, b;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 0; i
< n; i++)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&a,&b);
x.push_back(a);
y.push_back(b);
}
printf("%.3lf\n",findArea(x,y));
return 0;
}
Algorithm realization – classes
#include <stdio.h>
class Point
{
private:
double x, y;
public:
Point(double x = 0, double
y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {};
double GetX()
{
return x;
}
double GetY()
{
return y;
}
// cross product
double operator* (const Point &p)
{
return this->x *
p.y - this->y * p.x;
}
};
class Shape
{
protected:
Point *p;
int size;
public:
Shape(int size = 0) : size(size)
{
p = new Point[size+1];
}
~Shape()
{
delete[] p;
}
};
class Polygon : public
Shape
{
public:
Polygon(int n = 0) : Shape(n)
{};
void ReadPoints(void)
{
double x, y;
for(int i = 0; i <
size; i++)
{
scanf("%lf %lf",&x,&y);
p[i] =
Point(x,y);
}
p[size] = p[0];
}
double Area(void)
{
double s = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <
size; i++)
s += p[i] *
p[i+1];
return (s < 0) ? -s/2 : s/2;
}
};
int n;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
Polygon p(n);
p.ReadPoints();
printf("%.3lf\n",p.Area());
return 0;
}