904. Increase by 2
The sequence
of integers is given. Increase each its non-negative element by 2.
Input. The
first line contains the number of elements n (n
≤ 100). The second line contains the sequence of
integers, with each element not
exceeding 100 in absolute value.
Output. Print n integers in a single line – the new elements of the sequence, in their original order.
|
Sample
Input |
Sample
Output |
|
4 1 2 3 -4 |
3 4 5 -4 |
SOLUTION
loops
Algorithm analysis
The problem can be solved both
with and without an array. Sequentially read the numbers and increment each non-negative
element by 2.
Algorithm implementation
Read
the input value of n.
scanf("%d",&n);
Sequentially read n integers.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&val);
If the number val is non-negative, increase it by 2.
if (val >=
0) val +=2;
Print the number val after the modification.
printf("%d
",val);
}
printf("\n");
Algorithm implementation – array
Declare
an array.
int m[101];
Read
the input data.
scanf("%d",&n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",&m[i]);
Iterate
through the elements of an array. Increase each non-negative element by 2.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (m[i]
>= 0) m[i] = m[i] + 2;
Print the answer – the
resulting array.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d
",m[i]);
printf("\n");
Algorithm implementation – vector, push_back
Read
the input data.
scanf("%d",&n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&val);
m.push_back(val);
}
Iterate
through the elements of an array. Increase each non-negative element by 2.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (m[i]
>= 0) m[i] = m[i] + 2;
Print the answer – the
resulting array.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d
",m[i]);
printf("\n");
Algorithm implementation – vector,
resize
Read
the input data.
scanf("%d",&n);
m.resize(n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",&m[i]);
Iterate
through the elements of an array. Increase each non-negative element by 2.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (m[i]
>= 0) m[i] = m[i] + 2;
Print the answer – the
resulting array.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d
",m[i]);
printf("\n");
Algorithm implementation – pointers
#include <stdio.h>
int i, n;
int *m;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
// allocate mamory
m = new int[n];
// read the array
for (i = 0; i
< n; i++)
scanf("%d",&m[i]);
// process the array
for (i = 0; i
< n; i++)
if (m[i]
>= 0) m[i] = m[i] + 2;
// print the array
for (i = 0; i
< n; i++)
printf("%d
",m[i]);
printf("\n");
// free the memory
delete[] m;
return 0;
}
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int val = con.nextInt();
if (val >= 0) val += 2;
System.out.print(val + " ");
}
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}
Java implementation – array
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int m[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
m[i] = con.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (m[i] >= 0) m[i] += 2;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(m[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}
Java implementation –
ArrayList
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
ArrayList<Integer> m = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int val = con.nextInt();
m.add(val);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (m.get(i) >= 0) m.set(i,m.get(i)+2);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(m.get(i) + " ");
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
n = int(input())
lst = list(map(int,input().split()))
Iterate through the elements of a list. Increase each non-negative element by 2.
for i in
range(n):
if
lst[i] >= 0:
lst[i] = lst[i]
+ 2
Print
the answer – the
list lst.
print(*lst)
Python implementation – create a list
Read
the input data.
n = int(input())
list
= list(map(int,input().split()))
Create
the resulting list p. Increase each non-negative element of the list lst
by 2.
p = [x + 2 if x >= 0 else x for
x in lst]
Print the answer.
print(*p)
Python implementation
– map
n = int(input())
lst = map(int,input().split())
Declare a function f defined as follows:
f(n) = 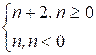
def f(n):
if
n >= 0:
return
n + 2
return
n
Apply the function f to each element of the list lst.
res = list(map(f,lst))
Print the list res.
for x in res:
print(x, end="
")