911. Quadratic
equation
Solve the
quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c
= 0 (a ≠ 0).
Input. One line contains three integers – the coefficients
of the quadratic equation a, b, and c. The absolute values of all coefficients do not exceed 100.
Output. Print on a
single line:
·
“No roots” if the equation has no roots;
·
“One root:” followed by the root, separated by a
space, if the equation has one root;
·
“Two roots:” followed by the smaller root and the
larger root, separated by a space, if the equation has two roots.
It is guaranteed
that if solutions exist, all roots are integers.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
1 -5 6 |
Two roots: 2
3 |
|
|
|
|
Sample input 2 |
Sample output 2 |
|
1 2 10 |
No roots |
SOLUTION
mathematics
Algorithm analysis
The task is to solve the
quadratic equation using the formula
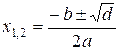 ,
,
where d is the discriminant of the quadratic equation, equal to b2 – 4ac.
Depending on the sign of
the discriminant, there are three possible cases:
·
d < 0: the equation has no
roots;
·
d = 0: the equation has one
root;
·
d > 0: the equation has two
roots, which should be printed in ascending order.
Algorithm implementation
Since
the coefficients of the equation and its roots (if they exist) are integers,
all computations will be performed using integers. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
Compute the discriminant of the
quadratic equation.
d = b * b - 4 *
a * c;
Depending on the sign of
the discriminant, print the answer.
if (d < 0)
printf("No
roots\n");
else if
(d == 0)
{
x1 = -b / (2 * a);
printf("One
root: %d\n", x1);
}
else
{
x1 = (-b - sqrt(d)) / (2 * a);
x2 = (-b + sqrt(d)) / (2 * a);
printf("Two
roots: ");
if (x1 <
x2)
printf("%d
%d\n", x1, x2);
else
printf("%d
%d\n", x2, x1);
}
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String []args)
{
Scanner
con = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = con.nextInt();
int b = con.nextInt();
int c = con.nextInt();
int d = b * b - 4 * a * c;
double x1 = (-b - Math.sqrt(d)) / (2 * a);
double x2 = (-b + Math.sqrt(d)) / (2 * a);
if (d == 0)
System.out.printf("One root:
%.0f\n", x1);
else if (d < 0)
System.out.printf("No
roots\n");
else if (x1 < x2)
System.out.printf("Two roots: %.0f
%.0f\n", x1, x2);
else
System.out.printf("Two roots: %.0f
%.0f\n ", x2, x1);
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
import math
Since
the coefficients of the equation and its roots (if they exist) are integers,
all computations will be performed using integers. Read the input data.
a, b, c = map(int, input().split())
Compute the discriminant of the
quadratic equation.
d = b * b - 4 * a * c
Depending on the sign of
the discriminant, print the answer.
if d < 0:
print("No roots")
elif d == 0:
x1 = -b // (2 * a)
print("One root:", x1)
else:
x1 = int((-b - math.sqrt(d)) // (2
* a))
x2 = int((-b + math.sqrt(d)) // (2
* a))
print("Two roots:", min(x1, x2), max(x1, x2))