974. Floyd
– 1
A complete
directed weighted graph is given by its adjacency matrix. Construct a matrix of
the shortest paths between all pairs of its vertices. It is guaranteed that the
graph has no cycles of negative weight.
Input. The first line contains the number of vertices n (1 ≤ n
≤ 100) in the graph. Each of the next n lines
contains n integers and describes the adjacency matrix of the
graph (the j-th
number in the i-th row corresponds
to the weight of the edge from vertex i to
vertex j). All numbers by the
absolute value do not exceed 100. The diagonal elements of the matrix are
always zeros.
Output. Print n lines with n integers – the matrix of the shortest distances between all pairs
of vertices. The j-th number in the i-th
row should equal the weight of the shortest path from vertex i to vertex j.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
4 0 5 9 100 100 0 2 8 100 100 0 7 4 100 100 0 |
0 5 7 13 12 0 2 8 11 16 0 7 4 9 11 0 |
SOLUTION
graphs – Floyd – Warshall
Algorithm analysis
In this problem you must construct a
matrix of the shortest paths between all pairs of vertices in a graph. To do
this, the Floyd-Warshall algorithm should be implemented.
Example
The graph described in the
problem statement is as follows:
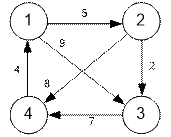
Algorithm realization
Store the
adjacency matrix of the graph in the array g.
#define MAX 101
int g[MAX][MAX];
The floyd function implements
the Floyd – Warshall algorithm.
void floyd(void)
{
int i, j, k;
for(k = 0; k
< n; k++)
for(i = 0; i
< n; i++)
for(j = 0; j
< n; j++)
if (g[i][k]
+ g[k][j] < g[i][j]) g[i][j] = g[i][k] + g[k][j];
}
The main part of the program. Read the input graph.
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(j = 0; j < n; j++)
scanf("%d",&g[i][j]);
Run the Floyd – Warshall algorithm.
floyd();
Print the matrix of the shortest
distances between all pairs of vertices.
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j
< n; j++)
printf("%d ",g[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int g[][];
static int n;
static void floyd()
{
for(int k = 0; k < n; k++)
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (g[i][k] + g[k][j] < g[i][j])
g[i][j] = g[i][k] + g[k][j];
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
n = con.nextInt();
g = new int[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
g[i][j] = con.nextInt();
floyd();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
System.out.print(g[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
con.close();
}
}
Python realization
The floyd function implements
the Floyd – Warshall algorithm.
def floyd():
for k in range(n):
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if g[i][k] + g[k][j] < g[i][j]:
g[i][j] = g[i][k] + g[k][j]
The main part of the program. Read the input graph.
n = int(input())
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
g[i] = list(map(int, input().split()))
Run the Floyd – Warshall algorithm.
floyd()
Print the matrix of the shortest
distances between all pairs of vertices.
for i in range(n):
print(*g[i])