981. Minimum spanning tree
Find the weight
of the minimum spanning tree for an undirected weighted connected graph.
Input. The first line contains the number of vertices n
and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 100, 1 ≤ m ≤ 6000) edges in the graph. Each of
the following m lines contains a triplet of numbers a, b, c,
where a and b are the vertex numbers connected by an edge, and c
is the weight of the edge (a positive integer not exceeding 30000).
Output. Print the weight of the minimum spanning tree.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
3 3 1 2 1 2 3 2 3 1 3 |
3 |
SOLUTION
graphs – minimum spanning
tree – Kruskal
Algorithm analysis
The task is to find the
weight of the minimum spanning tree using Kruskal’s algorithm.
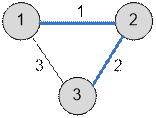
Example
The graph given in the example has the following form:
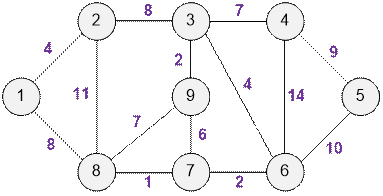
Exercise 1
Find the minimum spanning
tree and its weight for the following graph.
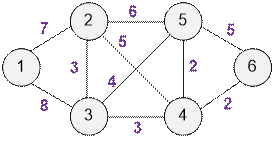
Exercise 2
Find the minimum spanning
tree and its weight for the following graph.
Algorithm implementation
Declare a structure for
the graph edge (a pair of vertices and the edge weight). Declare a vector of
edges e.
struct Edge
{
int u, v, dist;
};
vector<Edge> e;
Declare an array parent, that
will be used in the disjoint-set data structure.
vector<int> parent;
The
function Repr finds the representative of the set that contains vertex n.
int Repr(int n)
{
while (n != parent[n]) n = parent[n];
return n;
}
The function Union unites the sets containing elements x and y.
int Union(int x, int y)
{
x = Repr(x); y = Repr(y);
if (x == y) return 0;
parent[y] = x;
return 1;
}
The function lt is a comparator for sorting the edges.
int lt(Edge a, Edge b)
{
return (a.dist < b.dist);
}
The main part of the program.
Initialize the parent array.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
parent.resize(n + 1);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) parent[i] = i;
Read the edges of the graph.
e.resize(m);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
scanf("%d %d %d", &e[i].u, &e[i].v, &e[i].dist);
Sort the edges of the graph in increasing order of
weights.
sort(e.begin(), e.end(), lt);
Run Kruskal’s algorithm to construct the minimum
spanning tree.
res = 0;
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
if (Union(e[i].u,e[i].v)) res += e[i].dist;
Print the weight of the minimum spanning tree.
printf("%d\n",res);
Algorithm implementation – heuristics
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Edge
{
int u,
v, dist;
};
vector<Edge>
e;
vector<int>
parent, depth;
int i, n, m, res;
int Repr(int n)
{
if (n ==
parent[n]) return n;
return
parent[n] = Repr(parent[n]);
}
int Union(int x, int y)
{
x =
Repr(x); y = Repr(y);
if (x == y) return 0;
if
(depth[x] < depth[y])
swap(x, y);
parent[y] = x;
if
(depth[x] == depth[y])
depth[x]++;
return 1;
}
int lt(Edge a, Edge b)
{
return a.dist
< b.dist;
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d
%d", &n, &m);
parent.resize(n
+ 1);
depth.resize(n
+ 1);
for (i =
1; i <= n; i++)
{
parent[i] = i;
depth[i] = 0;
}
e.resize(m);
for (i = 0; i <
m; i++)
scanf("%d
%d %d", &e[i].u,
&e[i].v, &e[i].dist);
sort(e.begin(), e.end(),
lt);
res = 0;
for (i = 0; i <
m; i++)
if
(Union(e[i].u, e[i].v))
res += e[i].dist;
printf("%d\n",
res);
return 0;
}
Algorithm implementation – Prim
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#define MAX 101
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
using namespace std;
int i, n, m, a, b, c, res;
vector<vector<pair<int, int> > > g; // (to, dist)
int used[MAX], dist[MAX];
int Prim(int start)
{
memset(dist, 0x3F, sizeof(dist));
memset(used, 0, sizeof(used));
int cur = start, res = 0;
dist[cur] = 0;
used[cur] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (auto e : g[cur]) // cur -> to
{
int to = e.first;
int d = e.second;
if (!used[to] && (d
< dist[to]))
dist[to] = d;
}
int min = INF;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (!used[j] &&
(dist[j] < min))
{
min = dist[j];
cur = j;
}
used[cur] = 1;
res += dist[cur];
}
return res;
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
g.resize(n + 1);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &a, &b, &c);
g[a].push_back({ b, c });
g[b].push_back({ a, c });
}
res = Prim(1);
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
}
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
class Edge
{
int u, v, dist;
Edge (int u, int v, int dist)
{
this.u = u;
this.v = v;
this.dist = dist;
}
};
public class Main
{
static int mas[];
static int size[];
static int
Repr(int n)
{
if (n == mas[n]) return n;
return mas[n] = Repr(mas[n]);
}
static int
Union(int x, int y)
{
x = Repr(x); y = Repr(y);
if(x == y) return 0;
if (size[x]
< size[y])
{
int temp = x; x = y; y = temp;
}
mas[y] = x;
size[x] += size[y];
return 1;
}
public static class
MyFun implements Comparator<Edge>
{
public int
compare(Edge a, Edge b)
{
return a.dist - b.dist;
}
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int m = con.nextInt();
mas = new int[n+1];
size = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 1;
i <= n; i++)
{
mas[i] = i;
size[i] =
1;
}
Vector<Edge> v = new
Vector<Edge>();
for(int i = 0;
i < m; i++)
{
int x = con.nextInt();
int y = con.nextInt();
int dist = con.nextInt();
v.add(new
Edge(x, y, dist));
}
Collections.sort(v, new
MyFun());
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0;
i < m; i++)
if (Union(v.get(i).u, v.get(i).v) ==
1) res += v.get(i).dist;
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}