10042. LinkedList Cycle
Given a linked
list. Does it contain a cycle?
Definition of a
single linked list:
//Java
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode
next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
// C++
class ListNode
{
public:
int val;
ListNode
*next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
Implement a
function hasCycle that returns 1 if
linked list contains a cycle and 0 otherwise.
// Java
int hasCycle(ListNode head)
// C, C++
int hasCycle(ListNode *head)
Example
![]()
Function hasCycle returns 0 because
this linked list does not contain a cycle.
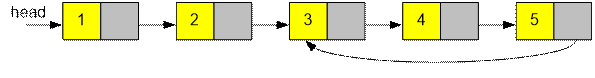
Function hasCycle returns 1 because
this linked list contains a cycle.
SOLUTION
linked list
Algorithm analysis
We’ll use two pointers p and q, moving them according to the principle of baby step giant step.
First, assign them to the start of the list. Next, iteratively move the first
pointer p forward one position in the
list, and the second pointer q move
two positions forward in the list. We stop if:
·
one of the pointers (this will be the pointer q) has reached the end of the list. Then the list has no cycle.
·
both pointers point to one element. This means that the fast
pointer q caught the slow pointer p, and the list contains a cycle.
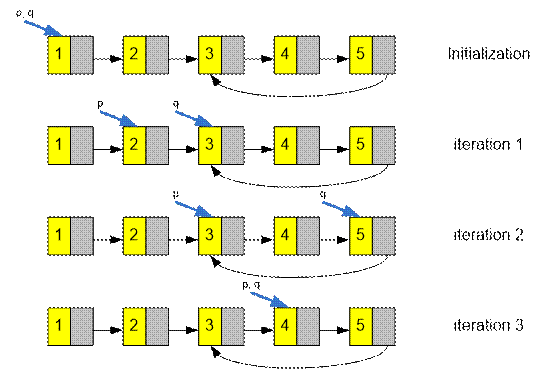
At the third
iteration, pointer q caught p, both pointers point to a vertex with
a value of 4. Cycle exists.
Algorithm realization
int hasCycle(ListNode *head)
{
if (head == NULL) return 0;
Set
up the pointers p and q to the start of the list.
ListNode* p =
head;
ListNode* q =
head;
While
there are at least two elements behind the q
pointer (the fast pointer can be moved two steps forward), we continue the loop.
while
(q->next && q->next->next)
{
p =
p->next;
q =
q->next->next;
If
pointers are equal, they point to the same memory location. The fast pointer q caught up the slow p, the list contains a cycle.
if (p
== q) return 1;
}
There
is no cycle, return 0.
return 0;
}
Java realization
int
hasCycle(ListNode head)
{
if (head == null) return 0;
ListNode p = head;
ListNode q = head;
while (q.next != null && q.next.next != null)
{
p = p.next;
q = q.next.next;
if (p == q) return 1;
}
return 0;
}