10047. LinkedList Intersection
Find the point of
intersection of two singly linked lists. Return the pointer to the node where
the intersection of two lists starts.
Definition of a single
linked list:
//Java
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
// C++
class ListNode
{
public:
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};
Implement a function intersection that
returns a pointer to the node where the intersection of two singly linked lists
starts.
// Java
ListNode intersection(ListNode l1, ListNode l2)
// C++
ListNode* intersection(ListNode
*l1, ListNode *l2)
Example
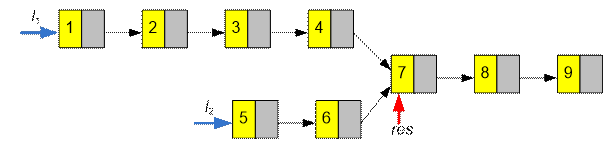
Function intersection must return a
pointer to the node with value 7.
SOLUTION
linked list
Algorithm analysis
Let's assume that input lists have the
same length. Set up to each of its heads a pointer. Move consecutively both
pointers one position to the right until they point to the same memory
location.
However, in our case, the lengths of the
lists may be different. Let lenA and lenB be the
lengths of the lists (they can be computed in O(n)). Let's set up two pointers to the heads of the lists. The
pointer, set on the head of a longer list, will be moved forward | lenA – lenB |
positions forward. Then solve the problem as if the lists have the same length.
Example
The length of the list l1 is lenA = 7. The length of the list l2 is lenB = 5.
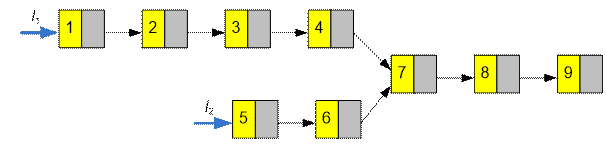
Set up the pointers a = l1, b = l2. Move the pointer a |7 – 5| = 2 positions
forward.
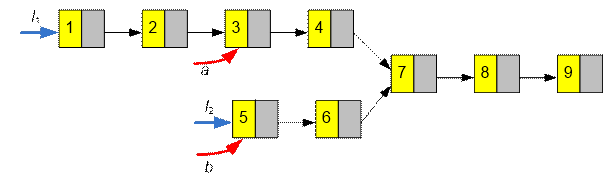
Step by step move the
pointers a and b one position
forward until they become equal. Once a
= b, the pointers will point to the
intersection point.
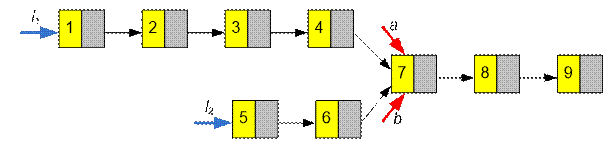
Algorithm realization
ListNode *intersection(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2)
{
Set up the
pointers a = l1, b = l2.
ListNode *a = l1, *b = l2;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
Find the length lenA of the list l1.
while (a != NULL)
{
lenA++;
a = a->next;
}
Find the length lenB of the list l2.
while (b != NULL)
{
lenB++;
b = b->next;
}
Move the
corresponding pointer | lenA – lenB | positions
forward.
a = l1; b = l2;
if (lenA > lenB)
{
for (int i = 0; i <
lenA - lenB; i++)
a = a->next;
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < lenB - lenA; i++)
b = b->next;
}
Move the
pointers a and b until they match.
while (a != b)
{
a = a->next;
b = b->next;
}
Return the pointer to the intersection point.
return a;
}