10379. Maximum
frequency stack
Design a data structure similar to a stack
that allows adding elements and removing the most frequent element from the
stack.
The following commands are supported:
·
push n –
add the number n to the stack;
·
pop – remove and print the most frequent
number currently in the stack. If there are multiple such numbers, remove and
output the one closest to the top of the stack.
Input. Consists of commands, one per line.
Output. For each pop operation, print
the result on a separate line.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
push 4 push 5 push 4 push 6 push 7 pop push 5 pop pop |
4 5 7 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
push 5 push 3 push 1 push 3 push 9 pop pop pop pop pop |
3 9 1 3 5 |
SOLUTION
data structures - stack
Algorithm analysis
For each number x,
we’ll keep track of how many times it appears in the stack using freq[x].
We’ll use a map as the data structure to store freq.
Declare an array of stacks vector<stack<int>> st, where st[i] contains the elements that
appear in the stack exactly i + 1 times (note that the array st
is zero-indexed). The order of elements in st[i] reflects the order in
which they were added to the stack.
Let the number x be added to the stack for the k-th time.
If the stack st[k – 1] has not been created yet, add it
using push_back. Then, place x on top of
the stack st[k – 1].
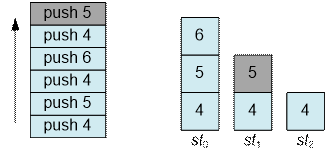
When removing an element,
it is necessary to extract the top element from the last non-empty stack.
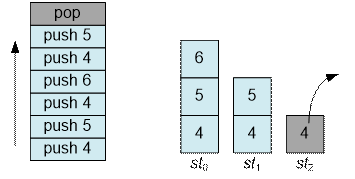
For example, if only pop
operations are performed from this point on, the elements will be removed from
the stack in the following order: 4, 5, 4, 6, 5, 4.
Example
Let
us examine the order in which elements are added to the array of stacks in the
following example.
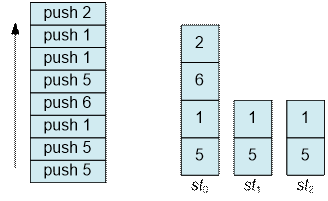
When
performing pop
operations, the elements will be extracted in the following order: 1, 5, 1, 5, 2, 6, 1, 5.
Algorithm implementation
To work with the frequency stack, we define a class called FreqStack.
class FreqStack
{
public:
Let’s declare:
·
a map freq, where freq[x] stores the number of
times element x appears in the stack;
·
an array of stacks st;
map<int, int> freq;
vector<stack<int>> st;
The push function adds element x to the stack.
void push(int x)
{
int f = freq[x];
freq[x] = f + 1;
if (f == st.size())
st.push_back(stack<int>());
st[f].push(x);
}
The pop function removes an element from the stack.
int pop()
{
int x = st.back().top();
st.back().pop();
if (st.back().empty())
st.pop_back();
freq[x]--;
return x;
}
};
The main part of the program. Read the input data and simulate the
behavior of the stack.
while (cin >> str)
{
if (str == "push")
{
cin >> n;
fs.push(n);
}
else // pop
cout << fs.pop() << endl;
}