10506. Connected components Adjacency list
Find the number of connected components in
the graph given by adjacency list.
Input. The first line contains the number of vertices n
(1 ≤ n ≤ 10000). Then n lines are given. The i-th
line contains the description of all edges, outgoing from the i-th
vertex. Description starts with the number of outgoing edges. Then given the
vertex numbers where the edges go. All vertices are numbered from 1 to
n.
Output. Print the number of connected components.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
6 2 5 6 0 0 1 5 2 1 4 1 1 |
3 |
SOLUTION
graphs
Algorithm analysis
Build an
adjacency list for the graph. Find the number of connected components
using depth first search.
Example
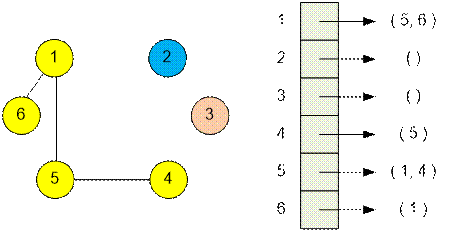
Graph contains
three connected
components.
Algorithm realization
Declare an adjacency list of graph g and an array used.
vector<vector<int>> g;
vector<int> used;
Finction dfs implements the depth first search
from the vertex v.
void dfs(int v)
{
used[v] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < g[v].size(); i++)
{
int to = g[v][i];
if (!used[to]) dfs(to);
}
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data. Build an adjacency
list.
scanf("%d", &n);
g.resize(n + 1);
used.resize(n + 1);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &k);
for (j = 0; j < k; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &x);
g[i].push_back(x);
}
}
Start the depth first search.
Count the number of connected components in the variable cnt.
cnt = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (used[i] == 0)
{
dfs(i);
cnt++;
}
Print the answer.
printf("%d\n", cnt);
Algorithm realization – union – find
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>>
g;
vector<int>
used, mas;
int i, j, n, x, k, cnt;
int Repr(int n)
{
while (n !=
mas[n]) n = mas[n];
return n;
}
void Union(int x, int y)
{
int x1 = Repr(x), y1
= Repr(y);
if (x1 == y1) return;
mas[x1] =
y1;
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",
&n);
g.resize(n + 1);
mas.resize(n + 1);
for (i = 1; i <=
n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",
&k);
for (j =
0; j < k; j++)
{
scanf("%d",
&x);
g[i].push_back(x);
}
}
for (i = 1; i <=
n; i++) mas[i] = i;
for (i =
1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (j =
0; j < g[i].size(); j++)
{
int to =
g[i][j];
Union(i, to);
}
}
cnt = 0;
for (i = 1; i <=
n; i++)
if (mas[i] ==
i) cnt++;
printf("%d\n",
cnt);
return 0;
}