10869. Building construction
You are given n buildings with
heights h1, h2, …, hn.
Your task is to make all buildings have the same height. You are allowed to
either remove bricks from buildings or add bricks to them. Adding or removing
one brick has a certain cost, which is specified individually for each
building.
Find the minimum total reconstruction cost
required to make all buildings have the same height k (where k is
any non-negative integer), that is, to satisfy the condition h1
= h2 = ... = hn = k.
For simplicity, assume that each building
is a vertical column made of identical bricks.
Input. The first line contains a single integer n (n
≤ 105) – the number of buildings.
The second line
contains integers – the heights of the buildings h1,
h2, …, hn (0 ≤ hi
≤ 104).
The third line contains n integers
c1, c2, ..., cn (0
≤ ci ≤ 104) – the cost of adding or
removing one brick for the corresponding building.
Output. Print a single integer – the minimum total cost
required to make all buildings have the same height.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
4 2 3 1 4 10 20 30 40 |
110 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
3 1 2 3 10 100 1000 |
120 |
SOLUTION
ternary search
Algorithm analysis
Sort the buildings by height so that h1 ≤ h2
≤ …≤ hn. Buildings with the same heights are sorted by
increasing cost of adding / removing.
Find the cost for which we can make the height of all houses
equal to hx (1 ≤
x ≤ n). It is equal
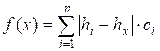
The function f(x) is concave and has a global minimum, that can be
found with a ternary search.
Example
Consider the first example. Sort buildings by height:
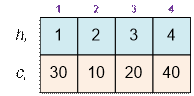
Find the value of the function f(x) for all heights:
·
f(1) = (1 – 1) * 30 + (2 – 1) * 10 + (3 – 1) * 20 + (4 – 1) * 40
= 170,
·
f(2) = (2 – 1) * 30 + (2 – 2) * 10 + (3 – 2) * 20
+ (4 – 2) * 40 = 130,
·
f(3) = (3 – 1) * 30 + (3 – 2) * 10 + (3 – 3) * 20
+ (4 – 3) * 40 = 110,
·
f(4) = (4 – 1) * 30 + (4 – 2) * 10 + (4 – 3) * 20 + (4 – 4) * 40
= 130
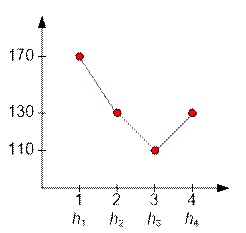
The minimum of the function f(x) is achieved at x = 3, while f(3) = 110.
Algorithm implementation
Each building has a height h
and the cost cost of adding or removing
a floor. The information about all buildings is stored in the
array b.
#define MAX 100001
struct Building
{
int h, cost;
};
Building b[MAX];
The
function cmp is a comparator for sorting buildings. Buildings are
sorted by increasing height. If the heights of the buildings are the same, then
sort them by increasing cost.
int cmp(Building a, Building b)
{
if (a.h == b.h)
return a.cost < b.cost;
return a.h < b.h;
}
The function f computes
the cost to make all buildings equal to the height of the building number x.
long long f(int x)
{
long long ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ret += 1LL * abs(b[x].h - b[i].h) * b[i].cost;
return ret;
}
The
function ternary_search uses the ternary search to
find the value of x ∈ [left; right] for which f(x) is minimal. Initially, the search range is [left; right] = [1; n].
long long ternarySearch(int left, int right)
{
while (right - left >= 3)
{
int a = left + (right - left) / 3;
int b = left + 2 * (right - left) / 3;
if (f(a) > f(b))
left = a;
else
right = b;
}
The
difference between left and right does not exceed 3. In this case, the minimum of f(x)
on the interval [left; right] is found by exhaustive search.
long long res = f(left++);
while (left <= right)
res = min(res, f(left++));
return res;
}
The main
part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &b[i].h);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &b[i].cost);
Sort the
buildings.
sort(b + 1,
b + n + 1, cmp);
Find and
print the answer. Buildings are numbered from 1 to n.
printf("%lld\n", ternarySearch(1, n));