11339. Divide into 2 groups
Divide the numbers 1, 2, ..., n into
two groups so that the absolute difference between the sums of the elements in
these groups is the smallest possible.
Input. One integer n (2 ≤ n ≤
105).
Output. In the first line, print two integers – the number of elements in the first and second groups.
In the second line, print the elements of
the first group, and in the third line – the
elements of the second group.
The elements within each group can be
printed in any order. Each number from 1 to n must
be included in exactly one of the groups.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
4 |
2 2 1 4 2 3 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
5 |
3 2 1 2 4 3 5 |
SOLUTION
greedy
Algorithm analysis
Note that if the
numbers n and n – 3 are placed in one group, and n – 1 and n – 2 are placed in the other (so that the sum of
numbers in each group is equal), the problem reduces to a similar problem of
smaller size, namely, dividing the numbers 1, 2, ..., n – 4 into two groups.
For n ≤ 3, the numbers are divided
into groups as follows:
·
If three numbers 1, 2, 3 remain, they can be divided into two
groups: {1, 2} and {3}.
·
If two numbers 1, 2 remain, they can be divided into groups: {1} and {2}.
The difference between the sums of the groups will be 1.
·
If one number 1 remains, it can be placed in either group.
The difference between the sums of the groups will be 1.
If the sum of all numbers
from 1 to n is even, they can be divided into two groups with equal
sums.
If the sum of all numbers
from 1 to n is odd, they can be divided into two groups with a sum
difference of 1.
Example
Let n = 10. The numbers are placed
into groups as follows:
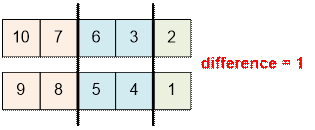
Let n = 11. The numbers are placed
into groups as follows:
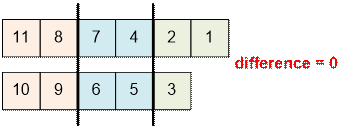
Algorithm implementation
Read
the input value n.
scanf("%d", &n);
Initialize
the initial sums of the numbers in the groups, s1 and s2,
to 0.
s1 = s2 = 0;
Iterate
through the numbers from n down to 1.
for (i = n; i > 0; i--)
If s1
< s2, place
the number i into the first group. Otherwise, place the number i
into the second group.
if (s1 < s2)
{
s1 += i;
a.push_back(i);
}
else
{
s2 += i;
b.push_back(i);
}
Print
the sizes of the groups.
printf("%d %d\n", a.size(), b.size());
Print
the numbers of the first group.
for (i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\n");
Print
the numbers of the second group.
for (i = 0; i < b.size(); i++)
printf("%d ", b[i]);
printf("\n");