11456. Next greater element
An array of integers is given. For each
element, you need to find the next greater element – the first element
to the right that is strictly greater than the current one.
If there is no next greater element for a
particular item, print -1.
Input. The first line contains a positive integer n (n
≤ 105).
The second line contains n positive
integers, each not exceeding 109.
Output. For each element of the input array, print its next
greater element. If there is none, print -1.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
10 5 3 8 5 7 4 2 1 3 7 |
8 8 -1 7 -1 7 3 3 7 -1 |
SOLUTION
stack
Algorithm analysis
Let’s declare a stack of
integers that will be used to store information about the next greater
elements. We’ll process the elements of the array a sequentially – from
right to left. When processing the element at index i:
·
Remove from the stack all numbers less than or equal to a[i];
·
If the stack is not empty, the number on top of the stack is the
next greater element for a[i]; if the stack is empty, assign -1
as the next greater element;
·
Then, push a[i] onto the stack.
At any moment, the stack
contains numbers in decreasing order. When the next number is processed, all
elements less than or equal to it are removed from the stack, and then this
number is pushed onto the top of the stack.
Example
Let’s take a look at how the
elements are processed using an example.
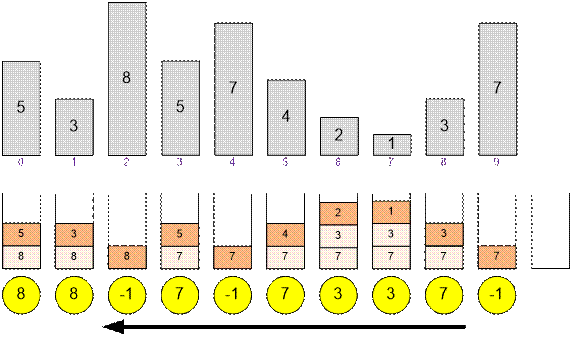
Algorithm implementation
Read
the input data.
scanf("%d", &n);
m.resize(n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &m[i]);
Process
the numbers sequentially from right to left.
for (i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
Remove
from the top of the stack all numbers less than or equal to m[i].
while (!s.empty() && (s.top() <= m[i])) s.pop();
The
next greater element after m[i] is the number on top of the stack. If
the stack is empty, store -1 in the result array res.
if
(s.empty()) res.push_back(-1);
else
res.push_back(s.top());
Push
the number m[i] onto the stack.
s.push(m[i]);
}
Reverse
and print the resulting array.
reverse(res.begin(),
res.end());
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", res[i]);
printf("\n");
Python implementation
Read
the input data.
n = int(input())
m = list(map(int, input().split()))
Initialize
the lists.
res = []
s = []
Process
the numbers sequentially from right to left.
for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
Remove
from the top of the stack all numbers less than or equal to m[i].
while s and s[-1] <= m[i]:
s.pop()
The
next greater element after m[i] is the number on top of the stack. If
the stack is empty, store -1 in the result array res.
if not s:
res.append(-1)
else:
res.append(s[-1])
Push
the number m[i] onto the stack.
s.append(m[i])
Reverse
and print the resulting list.
res.reverse()
print(*res)