1209. Function
with factorials
For the given even positive integer n find the value of
f(n) = 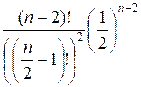
Input. Even
positive integer n (1 £ n
£ 100000).
Output. Print
the value of f(n) with four digits
after the decimal point.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
4 |
0.5000 |
SOLUTION
mathematics
Algorithm analysis
Take the logarithm of equation f(n) = 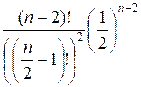 :
:
ln f(n) = ln(n – 2)! – 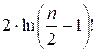 –
– ![]()
Calculate the right part of equation and apply the
exponential function base e to it. You will get f(n). Logarithm of
factorial can be computed as the sum of logarithms:
ln n! = ln 1 + ln 2
+ ln 3 + … + ln n
Algorithm realization
Declare
the global arrays.
#define MAX 100001
double lf[MAX], ans[MAX];
Fill the array lf, where lf[i] = lni!.
res = lf[1] = 0.0;
for(res = 0, i = 2; i < MAX; i++)
{
res += log((double)i);
lf[i] = res;
}
Fill the array ans, where ans[i] = f(i).
for(i = 2; i < MAX; i += 2)
{
res = lf[i/2-1];
res = lf[i-2] - (i - 2) * log(2.0) - res - res;
// res = ln f(i)
ans[i] = exp(res);
}
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("%.4lf\n",ans[n]);
Java realization
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main
{
public static final int MAX = 100001;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner
con = new Scanner(System.in);
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(System.out,true);
int i, n = con.nextInt();
double lf[] = new double[MAX],
ans[] = new double [MAX];
double res = lf[1] = 0.0;
for(res = 0, i = 2; i < MAX; i++)
{
res += Math.log(i);
lf[i]
= res;
}
for(i = 2; i < MAX; i += 2)
{
res =
lf[i/2-1];
res =
lf[i-2] - (i - 2) * Math.log(2.0) - res - res;
ans[i] = Math.exp(res);
}
out.printf(Locale.US,"%.4f\n",ans[n]);
}
}