1283. Banking reform
According to unconfirmed
rumors the banking reform is approaching, and you decide to make for it some
proposals – and what if they suddenly will be accepted, and even you will be
payed for these ideas?
Your idea is to change the
denominations in coin circulation. By your opinion, it should be
coins 1, 5, 10, 25 and 50 and how to call
the petty cash – let the central bank decides.
However, the Central Bank
has immediately demanded you to provide information about how many ways are
there to represent in cash the given amount of money up
to 7489 inclusive. Why up to this amount? And how the bank will name
them? But who knows: the bankers have their quirks, we also name them for
simplicity, just coins.
For example, an amount of 11
units can be represented in the form 10 * 1 coin
+ 1 * 1 coin, or 5 * 2 coins
+ 1 * 1 coin, or 5 * 1 coin
+ 1 * 6 coins or 11 * 1 coin, i.e.
total in four ways.
Your task is to write a
program to count the number of ways – to quickly respond to any request from
the bankers.
Input. Each line contains one
positive integer – the next bank request.
Output. For each request print on a
separate line the required number of ways to provide a specified amount.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
11 5 26 |
4 2 13 |
SOLUTION
dynamic programming
Algorithm analysis
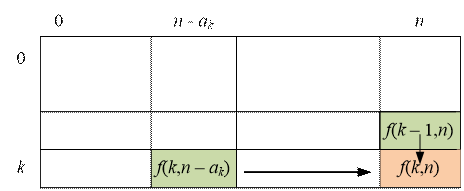
Let f(k, n) be the number of
ways to make up the sum n using the first k denominations of coins. It equals to the number
of ways to make up the sum of n using the first (k – 1) denominations only (that is,
without using the k-th denomination)
plus the number of ways to make up the sum (n – ak)
using k denominations.
We have the relation:
f(k,
n) = f(k – 1, n) + f(k, n
– ak)
Initially set f(0, 0) = 1,
f(0, n) = 0, n > 0.
Example
The sum s = 11 can
be represented in 4 ways:
1)
10 + 1
2)
5 + 5 + 1
3)
5 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1
4)
1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 +
1
|
|
k \ n |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
|
start |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
c = 1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
c = 5 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
|
c = 10 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
4 |
The
denominations of 25 and 50 cents will not affect the result for the amount of
11 cents.
For example,
consider the equality f (2, 10) = f (1, 10) + f (2, 5). It means that the
number of ways to
represent number 10 using two denominations of coins 1 and 5 includes:
·
f(1, 10) = 1, number of ways to represent 10
with one denomination
1 (10 = 1 + 1 + 1 + … + 1).
·
f(2, 5) = 2, number of ways to represent 5 with two denominations 1 and 5 (5 = 1 +
1 + 1 + 1 + 1 and 5 = 5).
Algorithm realization
Declare the
arrays.
#define MAX 7500
long long mas[MAX];
int
coins[11] = {1,5,10,25,50};
The main part
of the program.
memset(mas,0,sizeof(mas)); mas[0] = 1;
for(i
= 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for(j =
coins[i]; j < MAX; j++)
mas[j] += mas[j - coins[i]];
}
Read the input data and print the result.
while(scanf("%d",&n) == 1)
printf("%d\n",mas[n]);
Algorithm realization – recursion
with memoization
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int i, j, n;
int dp[6][7500];
int a[6] = { 0,1,5,10,25,50 };
int f(int k, int n)
{
if (k == 0
&& n == 0) return 1;
if (k == 0 || n
< 0) return 0;
if (dp[k][n] !=
-1) return dp[k][n];
return dp[k][n] = f(k
- 1, n) + f(k, n - a[k]);
}
int main(void)
{
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
while (scanf("%d", &n) == 1)
printf("%d\n", f(5, n));
return 0;
}
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int dp[][] = new int[6][7500];
static int a[] = {0,1,5,10,25,50};
static int f(int k, int n)
{
if (k == 0
&& n == 0) return 1;
if (k == 0 || n < 0) return 0;
if (dp[k][n] != -1) return dp[k][n];
return dp[k][n] = f(k - 1, n) + f(k, n - a[k]);
}
public static void
main(String []args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 7500; j++)
dp[i][j] = -1;
while(con.hasNext())
{
int n = con.nextInt();
System.out.println(f(5,n));
}
con.close();
}
}