1482. Matrix multiplication
Given two square
matrices A and B of dimensions m × n and n × q respectively:
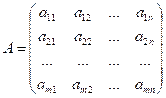 ,
, 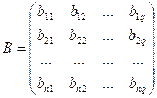
Then the matrix C of dimension m × q is called their product:
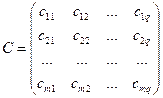
where:
![]() , (i = 1, 2, …, m; j
= 1, 2, …, q)
, (i = 1, 2, …, m; j
= 1, 2, …, q)
The operation of multiplication of two
matrices is feasible only if the number of columns in the first factor equals
to the number of rows in the second. In this case we say that the shape of the
matrices is consistent.
Given two matrices A and B.
Find their product.
Input. The first
line contains two positive integers na and ma – the dimensions of matrix A. Each
of the next na rows
contains ma numbers –
the elements aij of
matrix A. In (na + 2)-nd row two positive integers nb and mb are given – the dimensions of matrix B.
In the following nb lines mb numbers are given – the elements bij of matrix B. Dimensions of
the matrices do not exceed 100 × 100, all integers do
not exceed 100 by absolute value.
Output. Print in the first line the dimensions of the resulting matrix C: nñ and mc. In the next nñ rows print
mc space separated numbers
– the corresponding elements cij of
matrix C. If you cannot multiply matrices, in the first line print -1.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
2 3 1 3 4 5 -2 3 3 3 1 3 2 2 1 3 0 -1 1 |
2 3 7 2 15 1 10 7 |
SOLUTION
algebra
Algorithm analysis
Multiply matrices using
the formula:
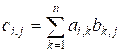 , where i = 1, 2, …, m; j
= 1, 2, …, q.
, where i = 1, 2, …, m; j
= 1, 2, …, q.
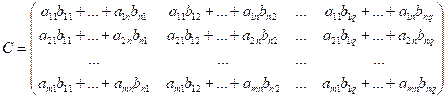
Example
The next product
of matrices is given in example:
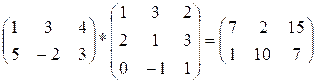
Algorithm realization
Store matrices A, B, C in two dimentional arrays
a,
b, c.
#define MAX 100
int a[MAX][MAX], b[MAX][MAX],
c[MAX][MAX];
Read the input matrices A and B.
scanf("%d %d",&na,&ma);
for(i = 0; i < na; i++)
for(j = 0; j < ma; j++) scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
scanf("%d %d",&nb,&mb);
for(i = 0; i < nb; i++)
for(j = 0; j < mb; j++) scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
Fill cells of matrix Ñ
with zeroes.
memset(c,0,sizeof(c));
If ma is not equal to nb, the matrices cannot be multiplied.
if (ma != nb)
{
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
Multiply the matrices using the above
formula.
for (i = 0; i < na; i++)
for (j = 0; j < mb; j++)
for (k = 0; k < ma; k++)
c[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
Print the resulting matrix Ñ.
printf("%d %d\n",na,mb);
for(i = 0; i < na; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j
< mb; j++)
printf("%d
",c[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
Algorithm realization – double
pointer
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 100
int na, ma, nb, mb;
int **a, **b, **c;
void Read(int **&matr, int n, int m)
{
matr = new int*[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
matr[i] = new int[m];
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
scanf("%d", &matr[i][j]);
}
}
void Mult(int **a, int **b, int **&c, int m, int n, int q)
{
c = new int*[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
c[i] = new int[q];
for (int j = 0; j < q; j++)
{
c[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
c[i][j] += a[i][k] *
b[k][j];
}
}
}
void Print(int **a, int n, int m)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
printf("%d ", a[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d %d", &na, &ma);
Read(a, na, ma);
scanf("%d %d", &nb, &mb);
Read(b, nb, mb);
if (ma != nb)
{
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
Mult(a, b, c, na, ma, mb);
printf("%d %d\n", na, mb);
Print(c, na, mb);
return 0;
}
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int na = con.nextInt();
int ma = con.nextInt();
int a[][] = new int[na][ma];
for (int i = 0; i < na; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < ma; j++)
a[i][j] = con.nextInt();
int nb = con.nextInt();
int mb = con.nextInt();
int b[][] = new int[nb][mb];
for (int i = 0; i < nb; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < mb; j++)
b[i][j] = con.nextInt();
con.close();
if (ma != nb)
{
System.out.println(-1);
return;
}
int c[][] = new int[na][mb];
for (int i = 0; i < na; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < mb; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < ma; k++)
c[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
System.out.println(na + " " + mb);
for (int i = 0; i < na; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < mb; j++)
System.out.print(c[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}