1506. Crossed
ladders
Along a narrow
street, there are two houses – one on the left and the other on the right.
A ladder of
length x feet is placed at
the base of the right house and leans against the house on the left. Another
ladder of length y feet
stands at the base of the left house and leans against the right house. The
ladders cross at a height of feet above the ground. Find the width
of the street.

Input. Each line represents a separate test case and
contains three positive real numbers: x,
y and c.
Output. For each test case, print one real number – the width of the
street, rounded to three decimal places.
|
Sampe
input |
Sample
output |
30 40 1012.619429 8.163332 310 10 310 10 1 |
26.033 7.000 8.000 9.798 |
SOLUTION
geometry – binary search
Algorithm analysis
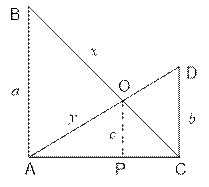
The tiangles AOP and ADC are similar: ![]() .
.
The triangles COP and CBA are also similar: ![]() .
.
![]()
Whence
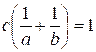 ,
, 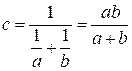 .
.
We’ll find the width of
the street d = AC using the binary search
method.
Initially, let 0 ≤ d ≤ min(x, y). Given the values of d, x and y, we can compute a, b and c. For fixed x and y, as d increases, the
value of c decreases.
Algorithm implementation
Read the input data for
each test case.
while(scanf("%lf
%lf %lf",&x,&y,&c) == 3)
{
Set the initial values: left = 0, right = min(x,y). During the
execution of the loop, the inequality left ≤ d ≤ right always holds.
left = 0;
if (x < y)
right = x; else right = y;
d = (left + right) / 2;
do
{
Compute the values of a, b, c.
a = sqrt(x*x - d*d); b = sqrt(y*y - d*d);
c1 = 1/(1/a + 1/b);
If the computed value c1 is less than
the given c, the upper bound of d should be
decreased. Otherwise, the lower bound should be increased.
if (c1 <
c) right = (left + right) / 2;
else
left = (left + right) / 2;
d = (left + right) / 2;
The computations are performed until the required accuracy
specified in the problem statement is reached – four decimal places.
} while (fabs(c1 - c) > 0.00001);
Print the answer.
printf("%.3lf\n",d);
}
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
con.useLocale(new Locale("US"));
while(con.hasNext())
{
double x = con.nextDouble();
double y = con.nextDouble();
double c = con.nextDouble();
double Left = 0, Right, a, b, c1;
if (x < y) Right = x; else Right = y;
double d = (Left + Right) / 2;
do
{
a = Math.sqrt(x*x - d*d);
b = Math.sqrt(y*y - d*d);
c1 = 1/(1/a + 1/b);
if (c1 < c) Right = (Left + Right) / 2;
else Left = (Left + Right) / 2;
d = (Left + Right) / 2;
} while (Math.abs(c1 - c) > 0.00001);
System.out.format(Locale.US,"%.3f\n",d);
}
}
}