1520. Odd Divisors
Let f(n) be the greatest odd divisor of a positive integer n. Find the sum:
f(1) + f(2) + ... + f(n)
Input. Each line
contains one positive integer n (n ≤ 109).
Output.
For each value of n, print the value
of the sum f(1) + f(2) + ... + f(n) on a separate line.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
7 1 777 |
21 1 201537 |
SOLUTION
recursion
Algorithm analysis
If n is odd, then f(n)
= n.
If n is even, then f(n)
= f(n / 2).
Let
g(n) = f(1) + f(2)
+ ... + f(n)
Consider the
partition of the set of positive integers from 1 to n into two subsets:
·
ODD – the set of odd numbers,
·
EVEN – the set of even numbers.
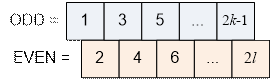
Among the positive integers
from 1 to n, there are exactly
·
k = ![]() odd numbers;
odd numbers;
·
l = ![]() even numbers
even numbers
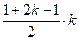
Then:
f(1) + f(3) +
f(5) + ... + f(2k
– 1) =
1
+ 3 + 5 + … + (2k – 1) =
![]() = k2
= k2
At the same time:
f(2) + f(4) +
f(6) + ... + f(2l)
=
f(1) + f(2) +
f(3) + ... + f(l)
=
g(l) = ![]()
To terminate the recursion,
let g(0) = 0. Thus:
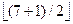
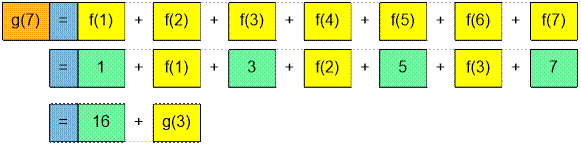
Example
Consider the first test
case where n = 7.
Among the positive integers
from 1 to 7 there are exactly:
·
k = ⌊(7 + 1) / 2⌋ = 4 odd numbers;
·
l = ⌊7 / 2⌋ = 3 even numbers.
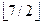
g(7) = 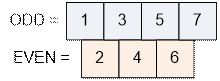 +
+ 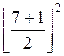 = 16 + g(3) =
= 16 + g(3) =
16 + 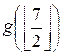 +
+ 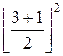 = 16 + 4 + g(1) = 16 +
4 + 1 = 21
= 16 + 4 + g(1) = 16 +
4 + 1 = 21
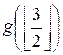
Algorithm
implementation
Implement the function g.
long long g(long long n)
{
long long k = (n + 1) / 2;
if (n == 0) return 0;
return k * k
+ g(n / 2);
}
The main part of the program. For each test case read the input
value of n and print g(n).
while(scanf("%lld",&n) == 1)
printf("%lld\n",g(n));
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class
{
static long g(long n)
{
long k = (n + 1) / 2;
if (n == 0) return 0;
return k * k + g(n / 2);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
while(con.hasNext())
{
long n = con.nextLong();
System.out.println(g(n));
}
}
}
Python implementation
Implement the function g.
def g(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
k = (n + 1) // 2
return k * k + g(n
// 2)
The main part of the program. For each test case read the input
value of n and print g(n).
for line in sys.stdin:
n = int(line)
print(g(n))