1605. Second digit of the number
Find the second
digit of an integer. Start counting digits from the leftmost position.
Input. One 64-bit integer n that contains
at least two digits. The number n can be negative.
Output. Print the second digit of n.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
43568 |
3 |
SOLUTION
loops
Algorithm analysis
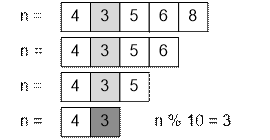
If the input
number n is negative, compute its absolute value – this will not change the second digit. Then divide the number
by 10 until it is greater than 99. The last digit of the resulting number will
be the second digit of the initial number.
Algorithm implementation
Read the input
number n. Since it is 64-bit number, use the long long type. If it is negative, then change its sign to the
opposite.
scanf("%lld",&n);
if (n < 0) n = -n;
Divide the number n
by 10 until it is greater than 99.
while (n > 99) n /= 10;
The last digit
of the resulting number will be the second digit of the initial number. Print it.
res = n % 10;
printf("%lld\n",res);
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String []args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
long n = con.nextLong();
if (n < 0) n = -n;
while (n > 99) n /= 10;
long res = n % 10;
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation – arithmetic approach
Read the input number n.
n = int(input())
If the number n
is negative, then change its sign to the opposite.
if n < 0: n = -n
Divide the number n
by 10 until it is greater than 99.
while n > 99:
n = n // 10
The last digit
of the resulting number will be the second digit of the initial number. Print it.
res = n % 10
print(res)
Python implementation – string
Read the input number n.
n = int(input())
Compute the absolute value of the number n. Then, convert it to a string, extract the first character (string indexing starts at zero), and convert it back to an integer.
res = int(str(abs(n))[1])
Print the answer.
print(res)