1658. Factorial
Find the
factorial of a number.
Input. One integer n (0 ≤ n
≤ 20).
Output. Print the value of n!
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
3 |
6 |
SOLUTION
elementary
Algorithm analysis
The factorial of
a number n is defined as the product of all positive integers from 1 to n:
n! = 1 * 2 * … * (n
– 1) * n
It is important to remember that the
factorial of zero is equal to one:
0! = 1
For example:
1! = 1;
2! = 1 * 2 = 2;
3! = 1 * 2 * 3 = 6;
4! = 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 = 24;
Notice that, for example
5! = (1 * 2 * 3 * 4) * 5 = 4! * 5;
100! = (1 * 2 * … * 99) * 100 = 99! * 100;
n! = 1 * 2 * … * (n
– 1) * n = (n – 1)! * n;
The factorial of
a number can be computed either using a loop or using recursion. In the latter case, one should utilize
the recursive formula:
fact(n) = 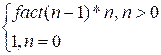
Algorithm implementation
Read the input value of n.
scanf("%lld",&n);
Compute the factorial of a number res = n! = 1 * 2 * 3 * … * n.
res = 1;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
res = res * i;
Print the answer.
printf("%lld\n",res);
Algorithm implementation – recursion
The fact function computes the factorial of the number n.
long long fact(long long n)
{
if (n == 0) return 1;
return fact(n - 1) * n;
}
The main part of the program. Read the input value of n.
scanf("%lld",&n);
Compute and print the answer.
res = fact(n);
printf("%lld\n",res);
Java implementation – recursion
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static long
fact(int n)
{
if (n ==
0) return 1;
return fact(n - 1)
* n;
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
long res = fact(n);
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation – loop
Read the input value of n.
n = int(input())
Compute the factorial of a number res = n! = 1 * 2 * 3 * … * n.
res = 1
for i in range(1,n+1):
res *= i Print the answer.
print(res)
Python implementation – recursion
The fact function computes the factorial of the number n.
def fact(n):
if n == 0: return 1
return n * fact(n - 1)
The main part of the program. Read the input value of n.
n = int(input())
Compute and print the answer.
print(fact(n))