1788. Inverse permutation
Given a permutation p, find its inverse p-1.
Input. The first line contains the order n (0 < n
≤ 20000) of the permutation p. The second
line contains the permutation p.
Output. Print the
inverse permutation p-1.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
3 2 3 1 |
3 1 2 |
SOLUTION
combinatorics - permutations
Algorithm analysis
Let p be a given permutation. Its
application means moving an element from position i to position p[i], i.e.,
the transformation i ® p[i] occurs. The inverse permutation
of p, denoted as pi,
will have the inverse transformation where p[i]
® i takes place. In other words, in the array pi, the number i
should be placed at position p[i] (pi[p[i]] = i).
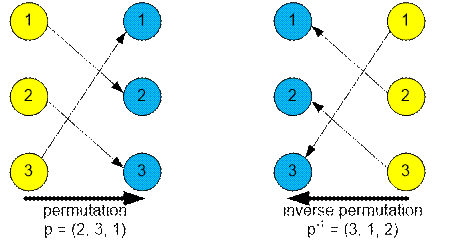
Example
Consider the permutation p = ![]() and its inverse p-1 =
and its inverse p-1 = ![]() . In the inverse permutation the edges are
oriented in the opposite direction.
. In the inverse permutation the edges are
oriented in the opposite direction.
Algorithm realization
The array p stores the input permutation, and the array pi stores the inverse permutation.
#define MAX 20010
int p[MAX], pi[MAX];
Read the input permutation.
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d",&p[i]);
Compute the inverse permutation.
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
pi[p[i]] = i;
Print the inverse permutation.
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d
",pi[i]);
printf("\n");
Python realization
The list p stores the input permutation, and the list pi stores the inverse permutation. Read the input
data.
n = int(input())
p = [0] + list(map(int, input().split()))
pi = [0] * (n + 1)
Compute the inverse permutation.
for i in range(1, n + 1):
pi[p[i]] = i
Print the inverse permutation.
for i in range(1, n + 1):
print(pi[i], end=" ")
print()