136. The segment
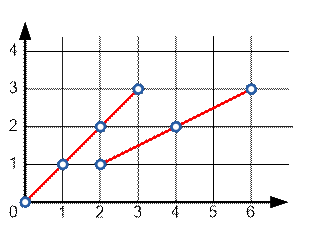
The endpoints of
the segment have integer coordinates. Count the number of points on the segment
with integer coordinates.
Input. Four integers represent the coordinates x1, y1,
x2, y2 of the endpoints of the segment. The coordinate
values do not exceed 2 * 109 in
absolute value.
Output. Print the number
of points on the segment with integer coordinates.
|
Sample input 1 |
Sample output 1 |
|
0 0 3 3 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
Sample input 2 |
Sample output 2 |
|
2 1 6 3 |
3 |
SOLUTION
GCD
Algorithm
analysis
If (x1,
y1) and (x2,
y2) are integer endpoints of the segment, then the number of integer points on it is equal to GCD ( |x2 – x1|, |y2
– y1| ) + 1.
Since the
coordinates of the segment endpoints do not exceed 2 * 109 in
absolute value, the absolute difference of coordinates |x2 – x1| and |y2
– y1| does not exceed 4
* 109. For example, if x1 = 2 * 109
and x2 = -2 * 109, then |x2 – x1| = 4 * 109. Therefore, 64-bit
integer type should be used for computations.
Example
For the first example, the answer is
1 + GCD ( |3 – 0|, |3 – 0| ) = 1 + GCD (3, 3) = 1 + 3 = 4
For the second example, the answer is
1 + GCD ( |6 – 2|, |3 – 1| ) = 1 + GCD (4, 2) = 1 + 2 = 3
Algorithm
implementation
The gcd function returns the greatest common
divisor of the numbers a and b.
long long gcd(long
long a, long
long b)
{
return (!b) ?
a : gcd(b,a % b);
}
Read
the input data.
scanf("%lld %lld %lld
%lld",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
Compute
the answer using the formula and print it.
res = gcd(labs(x2 - x1), labs(y2 - y1)) + 1;
printf("%lld\n",res);
Java implementation
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
The gcd function returns the greatest common
divisor of the numbers a and b.
static long
gcd(long a, long b)
{
if (b == 0) return a;
return gcd(b,a % b);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
Read
the input data.
long x1 = con.nextLong(),
y1 = con.nextLong(),
x2 = con.nextLong(),
y2 = con.nextLong();
Compute
the answer using the formula and print it.
long res = 1 + gcd(Math.abs(x2 - x1), Math.abs(y2 - y1));
System.out.println(res);
}
}
Python implementation
The gcd function returns the greatest common
divisor of the numbers a and b.
def gcd(a, b):
if a == 0: return
b
if b == 0: return
a
if a > b: return gcd(a % b, b)
return gcd(a, b %
a)
Read
the input data.
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, input().split())
Compute
the answer using the formula and print it.
res = gcd(abs(x2 - x1), abs(y2 - y1)) + 1
print(res)
Python implementation – gcd
To compute the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two
numbers, let’s use the gcd function built into the
Python language.
import math
Read
the input data.
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, input().split())
Compute
the answer using the formula and print it.
res = math.gcd(abs(x2 - x1), abs(y2 - y1)) + 1
print(res)