2098. Invertor
Given n integers. Print them in reverse order.
Input. First given number n (0 < n <
100), then given n integers.
Output. Print the given n integers in reverse order.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
7
2 4 1 3 5 3
1 |
1 3 5 3 1 4 2 |
SOLUTION
array
Algorithm analysis
Store the numbers in a linear array. Then print them in reverse order.
Let’s
consider a solution for reversing an array using the two-pointer
technique.
Set two variables i and j (we’ll call them pointers):
·
i at the beginning of the array (i = 1);
·
j at the end of the array (j = n);
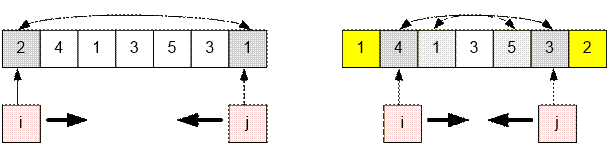
Next, start a while loop, in which:
·
the values of m[i] and m[j] are swapped;
·
then i is incremented by 1, and j is decremented by 1;
We continue the loop until the pointers i and j meet.
Note that
the values of m[i] and m[j]
can be swapped using an additional variable temp
by performing three operations:
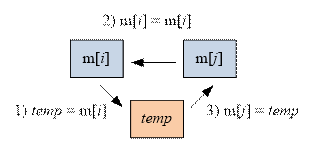
Algorithm implementation
Read the input data.
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d",&mas[i]);
Print the numbers in the reverse order.
for(i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
printf("%d
",mas[i]);
printf("\n");
Algorithm implementation –
reverse the array
#define MAX 110
int m[MAX];
Read the input data.
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d",&m[i]);
Reverse the
array using the two-pointer technique.
i = 1; j = n;
while(i < j)
{
temp = m[i]; m[i] = m[j]; m[j] = temp;
i++; j--;
}
Print the numbers.
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d
",m[i]);
printf("\n");
Algorithm implementation – dynamic
array
#include <stdio.h>
int n, i;
int *mas;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
mas = new int[n];
for(i = 0; i
< n; i++)
scanf("%d",mas+i);
int *p = mas,
*q = mas + n - 1;
while(p <
q)
{
int temp =
*p; *p = *q; *q = temp;
p++; q--;
}
for(i = 0; i
< n; i++)
printf("%d
",mas[i]);
printf("\n");
delete[] mas;
return 0;
}
Algorithm implementation – vector
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace
std;
int n, i;
vector<int> mas;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
mas.assign(n,0);
for(i = 0; i
< n; i++)
scanf("%d",&mas[i]);
for(i = n -
1; i >= 0; i--)
printf("%d
",mas[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Algorithm implementation – STL
reverse
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace
std;
int n, i;
vector<int> mas;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
mas.resize(n);
for(i = 0; i
< n; i++)
scanf("%d",&mas[i]);
reverse(mas.begin(),mas.end());
for(i = 0; i
< n; i++)
printf("%d
",mas[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Algorithm implementation – STL stack
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
using namespace
std;
int n, i, val;
stack<int> s;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i = 0; i
< n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&val);
s.push(val);
}
while(!s.empty())
{
printf("%d
",s.top());
s.pop();
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Java implementation – print the array from right to left
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int mas[] = new int[n];
for(int i = 0;
i < n; i++)
mas[i] = con.nextInt();
for(int i = n - 1;
i >= 0; i--)
System.out.print(mas[i] + "
");
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}
Java implementation – reverse
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int m[] = new int[n];
// Read data
for(int i = 0;
i < n; i++)
m[i] = con.nextInt();
// Reverse an
array
int i = 0,
j = n - 1;
while(i <
j)
{
int temp = m[i]; m[i] = m[j]; m[j] = temp;
i++; j--;
}
// Print the
reversed array
for(i = 0;
i < n; i++)
System.out.print(m[i] + "
");
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}
Java implementation – reverse with a function
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static int[]
reverse(int[] m)
{
int[] res = new int[m.length];
int i = 0,
j = m.length - 1;
while(i <
m.length)
{
res[i] = m[j];
i++; j--;
}
return res;
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int m[] = new int[n];
// Read data
for(int i = 0;
i < n; i++)
m[i] = con.nextInt();
// Reverse an
array
m = reverse(m);
// Print the
reversed array
for(int i = 0;
i < n; i++)
System.out.print(m[i] + "
");
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}
Java implementation – ArrayList – print the
array from right to left
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
ArrayList<Integer> mas = new
ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0;
i < n; i++)
mas.add(con.nextInt());
for(int i = n - 1;
i >= 0; i--)
System.out.print(mas.get(i) + "
");
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}
Java implementation – class, reverse
import java.util.*;
class Array
{
ArrayList<Integer> m;
Array()
{
m = new
ArrayList<Integer>();
}
public void add(int n)
{
m.add(n);
}
public void
Reverse()
{
int i = 0,
j = m.size() - 1;
while(i <
j)
{
Collections.swap(m,i,j);
i++; j--;
}
}
public void
Print()
{
for(int i = 0;
i < m.size(); i++)
System.out.print(m.get(i) + "
");
System.out.println();
}
};
public class Main
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
Array a = new
Array();
// Read data
for(int i = 0;
i < n; i++)
a.add(con.nextInt());
// Reverse an
array
a.Reverse();
// Print the
reversed array
a.Print();
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
Read the input data.
n = int(input())
lst = list(map(int, input().split()))
Print the numbers in the reverse order.
for i in range(n - 1,-1,-1):
print(lst[i], end = " ")
Python implementation – reverse
Read the input data.
n = int(input())
lst = list(map(int, input().split()))
Reverse the
list lst using the reverse function.
lst.reverse()
Print the reversed list.
print(*lst)