2129. Polar angle of a point
Find the polar
angle of the given point.
Input. Two integers are given – the Cartesian
coordinates of a point that does not coincide with the origin. The absolute
value of each number does not exceed 10000.
Output. Print one real number – the polar angle of
the given point in radians from the interval [0; 2π). The answer
should be rounded to 6 decimal places.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
2 3 |
0.982794 |
SOLUTION
geometry
Algorithm analysis
The polar coordinate system is a two-dimensional system in which every point on the plane is
uniquely determined by two numbers: the polar radius r and the polar angle φ (also called the azimuth
or the phase angle).
The radius r is the distance from the point to the center, or pole, of the
coordinate system. The angle φ
is the angle between the polar axis and the ray connecting the pole with the
point; it is measured counterclockwise from the ray corresponding to the
direction of 0° (this ray is called the polar axis).
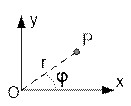
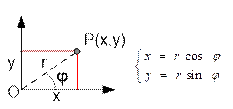
Let
point P have Cartesian coordinates (x, y) and polar coordinates (r, φ). Then the formulas for converting
from polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates are as follows:
![]()
The
function atan2(double y, double x) computes the arctangent of y/x and returns an angle in the interval (-π; π]. If x = 0 or both
arguments are zero, the function returns 0.
In
this problem, the polar angle must be given in the interval [0; 2π). Therefore, if the result of atan2 is negative,
you should add 2π to it.
Algorithm implementation
Read the input data.
scanf("%lf %lf",&a,&b);
The polar angle of a point is computed using the atan2 function.
res =
atan2(b,a);
If the result of atan2 is negative, you should add 2π to it, since the angle
must lie within the interval [0; 2π).
if (res < 0) res += 2*PI;
Print the answer.
printf("%.6lf\n",res);
Algorithm implementation
– class
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
class Point
{
private:
double x, y;
public:
Point(double
x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
void
ReadPoint(void)
{
scanf("%lf
%lf",&x,&y);
}
double
GetPolarAngle()
{
double res
= atan2(y,x);
if (res
< 0) res += 2*PI;
return res;
}
};
int main(void)
{
Point p;
p.ReadPoint();
printf("%.6lf\n",p.GetPolarAngle());
return 0;
}
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
double a = con.nextDouble();
double b = con.nextDouble();
double res = Math.atan2(b,a);
if (res < 0) res += 2 * Math.PI;
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
Read the input data.
import math
a, b = map(float,input().split())
The polar angle of a point is computed using the atan2 function.
res = math.atan2(b,a)
If the result of atan2 is negative, you should add 2π to it, since the angle
must lie within the interval [0; 2π).
if (res < 0) :
res += 2 * math.pi
Print the answer.
print("%.6f"
%res)