2248. Super minimum
Given n numbers. For every k consecutive numbers find the minimum
among them.
Input. First line contains the numbers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 106, 1 ≤ k ≤ n). Second line contains n integers
in the range from -32768 to 32767.
Output. For every k consecutive numbers print the
minimum among them.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
11 3
8 764 1 3 85
2 4 5 77 1 5 |
1 1 1 2 2 2 4 1 1 |
SOLUTION
queue
Algorithm analysis
Let’s implement a
queue that supports minimum. Add first k elements to the queue. Print the minimum in
the queue. Next, pop one element from the queue and add the next one to it. Thus, the queue
will contain the second k elements. Print the minimum again. Repeating the process of extracting
and inserting elements from / to the queue, we iterate over all sets of k consecutive
numbers. For each such set print the minimum.
Example
Consider the
process of calculating the minimums for a given example.
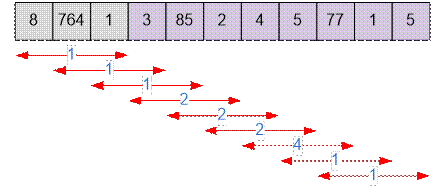
Algorithm realization
Let's implement a
queue
class that can
compue the minimum.
class Deque
{
private:
deque<int>
q, min;
public:
void pop(void)
{
if
(!q.empty())
{
if
(q.front() == min.front()) min.pop_front();
q.pop_front();
}
}
int getMin(void)
{
return
(min.empty()) ? 0 : min.front();
}
void push(int x)
{
q.push_back(x);
while(!min.empty()
&& x < min.back()) min.pop_back();
min.push_back(x);
}
};
The main part of the program. Read the input data. Declare the queue
d.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);
Deque d;
Push the first k elements to the queue.
for(i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
d.push(x);
}
Print the minimum of the current k elements. Read the next
number x. Pop a number from the queue and push next element x into it. Thus, the queue contains the next k consecutive
elements. Repeat the loop
until the queue contains the last k elements from n given numbers.
for(; i <= n; i++)
{
printf("%d
",d.getMin());
scanf("%d",&x);
d.pop();
d.push(x);
}
Print the minimum of the last k elements.
printf("%d\n",d.getMin());
Algorithm realization – class queue with arrays
#include <stdio.h>
int n, k, i, x;
class Deque
{
private:
int *value,
*mn;
int Bvalue,
Evalue, Bmn, Emn;
public:
Deque(int n =
150010)
{
value = new
int[n];
mn = new int[n];
Bvalue = Evalue = Bmn = Emn = 0;
}
~Deque()
{
delete[]
value;
delete[]
mn;
}
void pop(void)
{
if (Bvalue
!= Evalue)
{
if
(value[Bvalue] == mn[Bmn]) Bmn++;
Bvalue++;
}
}
int getMin(void)
{
return (Bmn
!= Emn) ? mn[Bmn] : 0;
}
void push(int x)
{
value[Evalue++] = x;
while((Bmn
!= Emn) && (x < mn[Emn-1])) Emn--;
mn[Emn++] = x;
}
};
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&n,&k);
Deque d(n);
for(i = 1; i
<= k; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
d.push(x);
}
for(; i <=
n; i++)
{
printf("%d
",d.getMin());
scanf("%d",&x);
d.pop();
d.push(x);
}
printf("%d\n",d.getMin());
return 0;
}
Algorithm realization – arrays
#include <cstdio>
#define MAX 150010
int n, k, i, v;
int q[MAX], m[MAX], qh, qt, mh, mt;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&n,&k);
qh = qt = mh = mt = 0;
for(i = 1; i
<= k; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&v);
q[qt++] = v;
while((mh
< mt) && (v < m[mt-1])) mt--;
m[mt++] = v;
}
printf("%d",m[mh]);
for(; i <=
n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&v);
if (q[qh]
== m[mh]) mh++; qh++;
q[qt++] = v;
while((mh
< mt) && (v < m[mt-1])) mt--;
m[mt++] = v;
printf("
%d",m[mh]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}