2351. Dijkstra
The directed weighted graph
is given. Find the shortest distance from one vertex to another.
Input. The first line contains
three integers n, s and f (1 ≤ n
≤ 2000; 1 ≤ s, f ≤ n),
where n is the number of graph
vertices, s is the initial vertex,
and f is the final vertex. Each
of the next n lines contains n integers – the matrix of weights
of the graph, where -1 means the lack of edge between the vertices,
and any nonnegative integer – the weight of the existing edge. The main
diagonal of the matrix contains zeroes.
Output.
Print the shortest distance from s to
f or -1 if the path
does not exist.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
3 1 2 0 -1
2 3 0
-1 -1 4
0 |
6 |
SOLUTION
graphs – Dijkstra
algorithm
Algorithm analysis
The graph is
given by the weight
matrix. To solve the problem, it is necessary to implement Dijkstra’s algorithm.
Example
The graph shown in
the sample has the form:
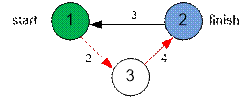
The shortest path from 1 to 2 equals to 2 + 4 = 6.
Algorithm realization
Implement Dijkstra’s algorithm using the weight matrix. Declare the global constants
and arrays.
#define MAX 2001
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
int g[MAX][MAX],
used[MAX], dist[MAX];
Function Relax relaxes the edge (i, j).
void
Relax(int i, int
j)
{
if (dist[i] + g[i][j] <
dist[j])
dist[j] = dist[i]
+ g[i][j];
}
The main
part of the program. Read the
input data.
scanf("%d %d %d",&n,&s,&f);
Initialization
of arrays.
memset(g,0x3F,sizeof(g));
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
memset(dist,0x3F,sizeof(dist));
dist[s]
= 0;
Read
the weight matrix.
for(i
= 1; i <= n; i++)
for(j
= 1; j <= n; j++)
scanf("%d",&g[i][j]);
Start Dijkstra’s algorithm. The source is at the vertex s.
for(i
= 1; i < n; i++)
{
min = INF; v = -1;
for(j = 1; j
<= n; j++)
if (used[j] == 0
&& dist[j] < min) {min = dist[j];
v =
j;}
Graph can be disconnected. If v = -1, then
the next vertex v is not found.
if (v
< 0) break;
Relax the edges outgoing from the
vertex v.
for(j = 1; j
<= n; j++)
if (used[j] == 0
&& g[v][j] != -1) Relax(v,j);
The shortest distance to the vertex v from the source s has already been calculated.
used[v] = 1;
}
Print the answer.
if
(dist[f] == INF) printf("-1\n");
else
printf("%d\n",dist[f]);
Java
realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static final int INFINITY = 2000000000;
static int g[][], used[], dist[];
static void Relax(int i, int j)
{
if (dist[i] + g[i][j] < dist[j])
dist[j] = dist[i] + g[i][j];
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int s = con.nextInt();
int f = con.nextInt();
g = new int[n+1][n+1];
for (int[] row: g) Arrays.fill(row, INFINITY);
used = new int[n+1]; Arrays.fill(used, 0);
dist = new int[n+1]; Arrays.fill(dist, INFINITY);
dist[s] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
g[i][j] = con.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
// find vertex
w with minimum d[w] among not used vertices
int min = INFINITY, v = -1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (used[j] == 0
&& dist[j] < min) { min = dist[j]; v = j; }
// no more
vertices to add
if (v < 0) break;
// relax all
edges outgoing from v
// process edge
v -> j
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (used[j] == 0
&& g[v][j] != -1) Relax(v, j);
// shortest
distance to v is found
used[v] = 1;
}
if (dist[f] == INFINITY) System.out.println(-1);
else System.out.println(dist[f]);
con.close();
}
}