2471. From adjacency matrix to the list of edges
The simple not
oriented graph is given by the adjacency matrix. Print its representation as a
list of edges.
Input. The
first line contains the number n (1
≤ n ≤ 100) of vertices in
a graph. Each of the next n lines
contains n elements – the description of
adjacency matrix.
Output. Print
the list of edges, ordered by the first vertex in a pair that describes an
edge.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
3 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 |
1 2 1 3 2 3 |
SOLUTION
graphs
Algorithm analysis
We will print a list of edges on fly, processing adjacency matrix line
by line from top to bottom, and each row from left to right. For each number
one in the adjacency matrix we print a pair of vertexes that define the
corresponding edge. These pairs of vertexes will be ordered by the first
vertex.
Example
Graph given in a sample, has a form:
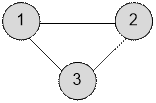
Algorithm realization
Read the adjacency matrix. As the graph is not oriented, we’ll print only the edges (i, j) for which i < j.
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i
= 1; i <= n; i++)
for(j
= 1; j <= n; j++)
{
scanf("%d",&val);
if (i < j
&& val == 1)
printf("%d
%d\n",i,j);
}
Java realization
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class
{
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
//Scanner
con = new Scanner(new FileReader ("2471.in"));
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
int val = con.nextInt();
if (i < j && val == 1)
System.out.println(i + " " +
j);
}
con.close();
}
}