273. Modular Exponentiation
Three positive integers x, n and m are given. Find the value of xn mod m.
Input. Three positive integers x, n, m (1 ≤ x ≤ 109, 1
≤ n ≤ 107,
2 ≤ m
≤ 109).
Output. Print one integer – the value of xn mod m.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
2 3 100 |
8 |
SOLUTION
exponentiation
Algorithm analysis
Exponentiation is a mathematical operation,
written as xn, involving two numbers, the
base x and the exponent or power
n. When n is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to repeated
multiplication of the base: that is, xn is the product of
multiplying n bases: xn = x * x
* … * x.
How can we compute xn for given x
and n? One option is to use one loop
with a time complexity of O(n). The linear time
algorithm will pass the time limit because
n ≤ 107.
Alternatively, you can use fast exponentiation:
xn = 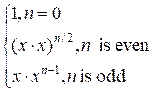
Algorithm realization
Let’s use the 64-bit integer type long long. Read the input
data.
scanf("%lld %lld %lld", &x, &n, &m);
Compute the
value of xn mod m using a loop.
res = 1;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
res = (res * x) % m;
Print the answer.
printf("%lld\n", res);
Algorithm realization – Fast
Exponentiation
The PowMod function finds the value of xn mod m.
long long powmod(long long x, long long n, long long m)
{
if (n == 0) return 1;
if (n % 2 == 0) return powmod((x * x) % m, n / 2, m);
return (x * powmod(x, n - 1, m)) % m;
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%lld %lld %lld", &x, &n, &m);
Compute and print the answer.
res = powmod(x,
n, m);
printf("%lld\n", res);
Realization
with classes
#include <stdio.h>
class Long
{
private:
long long value;
public:
static long long mod;
Long() : value(0) {}
Long(long long value) :
value(value) {}
void Read(void)
{
scanf("%lld",&value);
}
static void ReadMod(void)
{
scanf("%lld",&mod);
}
void Print(void)
{
printf("%lld\n",value);
}
bool IsOdd(void)
{
return value & 1;
}
Long operator* (const Long
&x)
{
return (value * x.value) % mod;
}
Long operator/ (const long long &x)
{
return value / x;
}
bool operator== (const long long &x)
{
return this->value
== x;
}
Long operator^ (Long n)
{
Long x(*this);
if (n == 0) return
Long(1);
if (n.IsOdd()) return
x * ((x * x) ^ (n/2));
return (x * x) ^ (n/2);
}
};
long long Long::mod = 0;
int main(void)
{
Long x, n, res;
x.Read();
n.Read();
Long::ReadMod();
res = x ^ n;
res.Print();
return 0;
}
Java realization
– linear complexity
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
long x = con.nextLong(),
n = con.nextLong(),
m = con.nextLong();
long res = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
res = (res * x) % m;
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Java realization – O(log2n)
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static long PowMod(long x, long n, long m)
{
if (n == 0) return 1;
if (n % 2 == 0) return PowMod((x * x) % m, n / 2, m);
return (x * PowMod(x, n - 1, m)) % m;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner
con = new Scanner(System.in);
long x = con.nextLong();
long n = con.nextLong();
long m = con.nextLong();
long res = PowMod(x,n,m);
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Java
realization – powMod
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner
con = new Scanner(System.in);
BigInteger x = con.nextBigInteger();
BigInteger n = con.nextBigInteger();
BigInteger m = con.nextBigInteger();
System.out.println(x.modPow(n,m));
con.close();
}
}
Java realization
(input/output files)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
//Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
Scanner con = new Scanner(new FileReader ("273.in"));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File("273.out"));
long x = con.nextLong(),
n = con.nextLong(),
m = con.nextLong();
long res = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) res = (res * x) % m;
//System.out.println(res);
out.println(res);
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
Python realization – pow
Read the input data.
x, n, m = map(int, input().split())
Compute and print the answer. Use the built-in function pow to evaluate the
expression xn mod m.
print(pow(x, n, m))
Python realization – loop
Read the input data.
x, n, m = map(int, input().split())
Compute the
value of xn mod m using a loop.
res = 1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
res = (res * x) % m
Print the answer.
print(res)