3981 . From adjacency matrix to adjacency
list
A simple directed graph is
given by its adjacency matrix. Print its representation as adjacency list.
Input. The first line contains the number n (1 ≤ n
≤ 100) of vertices in the graph. Each of the following n lines
contains n integers – the adjacency matrix. It is guaranteed that the
graph has no self-loops.
Output. Print n lines – the
adjacency list of the graph. In the i-th line, first print the number of
edges going out from vertex i, followed by the numbers of the vertices
they point to, in ascending order.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
5 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 |
1 3 2 1 3 1 5 2 1 2 2 1 2 |
SOLUTION
graphs
Algorithm analysis
Read the adjacency matrix
and build the adjacency list from it. Then, print the list.
Example
The graph from the example has the
following form.
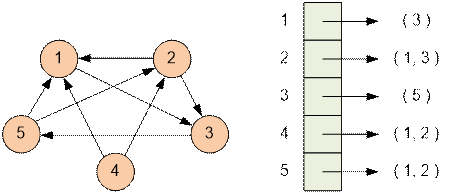
Algorithm implementation
Declare the adjacency list
of the graph.
vector<vector<int> > g;
Read the input data. The vertices of the graph are numbered from 1 to n.
Build the
adjacency list.
scanf("%d", &n);
g.resize(n + 1);
for (i = 1; i <= n;
i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n;
j++)
{
scanf("%d", &val);
if (val) g[i].push_back(j);
}
Print the adjacency list.
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
printf("%d", g[i].size());
for (int x : g[i])
printf(" %d", x);
printf("\n");
}
Java implementation
– array of ArrayList
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner
con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
ArrayList<Integer>[] g = new ArrayList[n+1]; // unchecked
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
g[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
int val = con.nextInt();
if (val == 1) g[i].add(j);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
System.out.print(g[i].size());
for (int j = 0; j < g[i].size(); j++)
System.out.print(" " + g[i].get(j));
System.out.println();
}
con.close();
}
}
Java implementation
– ArrayList of ArrayList
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
//Scanner con = new Scanner(new FileReader
("3981.in"));
Scanner
con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> g =
new
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
g.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
int val = con.nextInt();
if (val == 1) g.get(i).add(j);
}
//System.out.println(g);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
System.out.print(g.get(i).size());
for (int j = 0; j < g.get(i).size(); j++)
System.out.print(" " + g.get(i).get(j));
System.out.println();
}
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
Read the number of
vertices n. Declare the adjacency list g.
n = int(input())
g = [[] for _ in
range(n + 1)]
Read the adjacency matrix and build the adjacency list. The vertices of
the graph are numbered from 1 to n.
for i in range(1, n + 1):
row = list(map(int, input().split()))
for j in range(1, n + 1):
if row[j - 1]:
g[i].append(j)
Print the adjacency list.
for i in range(1, n + 1):
print(len(g[i]), *g[i])