4107. Totient
extreme
Given the positive integer n, find
the value of H that is computed by the following code:
H = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= n;
i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
H = H +
totient(i) * totient(j);
}
}
Totient or phi function, φ(n) is an arithmetic function that counts the number of positive integers
less than or equal to n that are
relatively prime to n. That is, if n is a positive integer, then φ(n) is
the number of such integers k (1 ≤
k ≤ n), for which gcd(n,
k) = 1.
Input. The first line contains the number of test cases
t (0 < t ≤ 106). It is followed by t
lines each containing a number n (0 < n
≤ 104).
Output. For each line produce one line that contains the value of H for the
corresponding n.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
2 3 10 |
16 1024 |
SOLUTION
Euler
function
Algorithm analysis
Let us rewrite the sum H as follows:
φ(1) * φ(1) + φ(1) * φ(2) + …
φ(1) * φ(n) +
φ(2) * φ(1) + φ(2) * φ(2) + …
φ(2) * φ(n) +
. . .
φ(n) *
φ(1) + φ(n) * φ(2) + …
φ(n) * φ(n)
=
φ(1) * (φ(1) + φ(2) + … φ(n)) +
φ(2) * (φ(1) + φ(2) + … φ(n)) +
. . .
φ(n) *
(φ(1) + φ(2) + … φ(n))
=
= (φ(1) + φ(2) + … φ(n))2
Let's implement a sieve that will calculate all values
of the Euler function from 1 to 104 and put them into the array fi.
Let's fill in the array of partial sums sum[i] = φ(1) + φ(2) + … φ(i). Next, for each input value of n, print sum[n] * sum[n].
Example
Consider
the arrays with values of Euler function fi and the array of partial
sums sum:
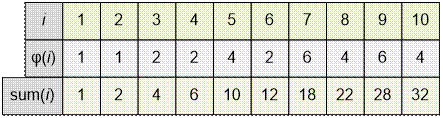
For n = 10 the answer is
(φ(1) + φ(2) + … φ(10))2 = sum[10]2 = 322 = 1024
Algorithm realization
Declare the working arrays fi
and sum where
·
fi[i] = φ(i);
·
sum[i] = φ(1) + φ(2) + … φ(i)
#define MAX 10001
long long
fi[MAX], sum[MAX];
Function FillEuler filles the array fi[i] with values of Euler function: fi[i] = φ(i), 1 ≤ i < MAX.
void FillEuler(void)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < MAX; i++) fi[i] = i;
for (i = 2; i < MAX; i++)
if (fi[i] == i)
for (j = i; j <
MAX; j += i)
fi[j] -= fi[j] / i;
Calculate the partial sums sum[i].
sum[0] = 0; sum[1] = 1;
for(i = 2; i < MAX; i++)
sum[i] = sum[i-1] + fi[i];
}
The main part of the program. Fill arrays fi and sum.
FillEuler();
Process tests test
cases.
scanf("%d",&tests);
while(tests--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
For each input value of n print
sum[n] * sum[n] = (φ(1)
+ φ(2) + … φ(n))2
res = sum[n] * sum[n];
printf("%lld\n",res);
}