4852. The shortest distance
The directed
graph is given. Find the shortest distance from the vertex x to other vertices of the graph.
Input. The first line contains two integers n and x (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000,
1 ≤ x ≤ n) – the number of vertices in a graph
and the starting vertex. Each of the next n
lines contains n numbers – the adjacency
matrix of the graph: the i-th
line and j-th column contains “1”,
if the vertices i and j are connected with the edge, and “0”,
if there is no edge between them. The main diagonal contains zeroes.
Output. Print the numbers d1, d2,
..., dn, where di is -1 if
there is no path from x to i, or the minimal distance from x to i
otherwise.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
outupt |
|
6 5 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 |
2 2 1 1 0 -1 |
SOLUTION
graphs, breadth first search
Algorithm analysis
In this problem it is
necessary to implement the breadth-first search to construct an array of
shortest distances dist from the source to all vertices. Since the number of
vertices is no more than 1000, the graph can be stored in an adjacency matrix.
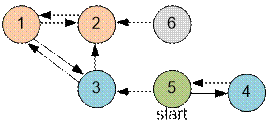
Example
The graph given in example have the form:
Algorithm realization
Declare an array
g for storing the graph, as well as additional used and dist arrays to
implement breadth-first search. dist[i]
contains the shortest
distance from source to vertex i.
#define MAX 1010
int g[MAX][MAX], used[MAX], dist[MAX];
Function bfs
runs breadth first search from vertex start.
The queue is implemented as a local array q
of size MAX (at any time, the number of vertices in the queue will be no more
than the number of vertices in the graph). Head
and Tail are pointers to the head and
the end of the
queue.
void bfs(int
start)
{
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
memset(dist,-1,sizeof(dist));
dist[start] = 0;
int q[MAX],
Head = 0, Tail = 1;
q[Head] = start; used[start] = 1;
while(Head
< Tail)
{
int v =
q[Head++];
If there is an edge from v to i,
and the vertex i is
not visited yet, then go to it (the edge (v, i) is a tree edge in
breadth first search).
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if
(g[v][i] && !used[i])
{
q[Tail++] = i;
used[i] = 1;
dist[i] = dist[v] + 1;
}
}
}
The main part of
the program. Read the input
data.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&x);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
scanf("%d",&g[i][j]);
Run the breadth first search from the
vertex x.
bfs(x);
Print the required shortest distances.
printf("%d",dist[1]);
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
printf("
%d",dist[i]);
printf("\n");
Algorithm realization – STL
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define MAX 1010
using namespace
std;
int i, j, n, x;
int g[MAX][MAX], dist[MAX];
void bfs(int
start)
{
memset(dist,-1,sizeof(dist));
dist[start] = 0;
queue<int>
q;
q.push(start);
while(!q.empty())
{
int v =
q.front(); q.pop();
for(int to = 1; to <= n; to++)
if
(g[v][to] && (dist[to] == -1))
{
q.push(to);
dist[to] = dist[v] + 1;
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&n,&x);
for(i = 1; i
<= n; i++)
for(j = 1; j
<= n; j++)
scanf("%d",&g[i][j]);
bfs(x);
for(i = 1; i
<= n; i++)
printf("%d
",dist[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Java
realization
import java.util.*;
//import java.io.*;
public class Main
{
static int n, x;
static int g[][];
static int dist[];
static void dfs(int start)
{
dist[start] = 0;
Queue<Integer> q = new
LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(start);
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
int v = q.poll();
for(int to = 1; to <= n; to++)
if ((g[v][to] == 1) && (dist[to] == -1))
{
q.add(to);
dist[to] = dist[v] + 1;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) // throws IOException
{
//Scanner
con = new Scanner(new FileReader ("4852.in"));
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
n = con.nextInt();
x = con.nextInt();
g = new int[n+1][n+1];
dist = new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(dist, -1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
g[i][j] = con.nextInt();
dfs(x);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
System.out.print(dist[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}