4853. The shortest path
An undirected graph is given. Find the
shortest path from vertex a to vertex b.
Input. The first line contains two integers n and m
(1 ≤ n ≤ 5 * 104, 1 ≤ m ≤ 105)
– the number of vertices and edges, respectively.
The second line contains two integers a
and b – the starting and ending vertices.
Each of the following m lines describe
an edge.
Output. If there is no path from a to b, print -1.
Otherwise, print the length l of the
shortest path on the first line, and on the second line print l + 1
numbers: the sequence of vertices along this path.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
4 5 1 4 1 3 3 2 2 4 2 1 2 3 |
2 1 2 4 |
SOLUTION
graphs – breadth first
search
Algorithm analysis
In this problem, you
should implement a breadth-first search (BFS), constructing an array of
shortest distances dist and an array of parents parent from the
source to all vertices. Since the number of vertices is around 50000, it is
efficient to store the graph as an adjacency list.
Example
The graph given in the
example has the following form:
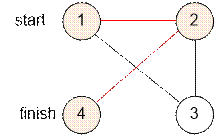
Algorithm implementation
Declare an
adjacency list g to store the graph, as well as the following additional
arrays:
·
dist[i] stores the shortest
distance from the source to vertex i,
·
parent[i] stores the parent of
vertex i during the breadth-first search.
vector<int> dist, parent;
vector<vector<int> > g;
The bfs function performs a breadth-first search starting
from the vertex start.
void bfs(int start)
{
// declare arrays
parent = vector<int>(n + 1, -1);
dist = vector<int>(n + 1, -1);
dist[start] = 0;
// initialize a queue
queue<int> q;
q.push(start);
while (!q.empty())
{
// remove vertex v from the queue
int v = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int to : g[v]) // there is an edge v
-> to
// if vertex v is not visited
if (dist[to] == -1)
{
q.push(to); // push to into the queue
dist[to] = dist[v] + 1; // recalculate the
shortest distance
parent[to] = v; // if v -> to, parent for to is v
}
}
}
The PrintPath
function prints the shortest path from the source to vertex v. Vertex v
is the starting point if parent[v] = -1.
void PrintPath(int v)
{
if (v == -1) return;
PrintPath(parent[v]);
printf("%d ", v);
}
The main part of the
program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
Create the adjacency list of the graph.
g.resize(n + 1);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &u, &v);
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
Start the breadth-first search from vertex a.
bfs(a);
If vertex b was not reached during the search (parent[b]
= -1), print -1.
if (parent[b] == -1)
printf("-1\n");
else
{
Otherwise, print the length of the shortest path to b
and the path itself.
printf("%d\n", dist[b]);
PrintPath(b);
}
Java ðåàëèçàöèÿ
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static ArrayList<Integer>[] g;
static int dist[], parent[];
static int n, m;
static void bfs(int start)
{
Arrays.fill(dist,-1);
dist[start] = 0;
Arrays.fill(parent,-1);
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(start);
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
int v = q.poll();
for(int i = 0; i < g[v].size(); i++)
{
int to = g[v].get(i);
if (dist[to] == -1)
{
q.add(to);
dist[to] = dist[v] + 1;
parent[to] = v;
}
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
n = con.nextInt(); m = con.nextInt();
int a = con.nextInt();
int b = con.nextInt();
g = new ArrayList[n+1];
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
g[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
dist = new int[n+1];
parent = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int u = con.nextInt();
int v = con.nextInt();
g[u].add(v);
g[v].add(u);
}
bfs(a);
if (parent[b] == -1)
System.out.println("-1");
else
{
System.out.println(dist[b]);
Vector<Integer> path = new
Vector<Integer>();
path.add(b);
while (parent[b] != -1)
{
b = parent[b];
path.add(b);
}
for (int i = path.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
System.out.print(path.get(i) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
con.close();
}
}