4856. The shortest path
The undirected weighted graph is given.
Find the shortest path between two given vertices.
Input. The first line contains two positive integers n
and m (n ≤ 2000, m ≤ 50000) – the number
of vertices and edges in a graph. The second line contains positive integers s
and f (1 ≤ s, f ≤ n, s ≠ f)
– the numbers of the vertices, the minimal length between which must be found.
Each of the next m lines contains three numbers bi, ei and wi –
the numbers of the ends of i-th edge and its
weight correspondingly (1 ≤ bi, ei
≤ n, 0 ≤ wi ≤
105).
Output. Print in the first line one number – the length of
minimal path between the vertices s and f.
Print in the second line all the vertices on the shortest path from s to f in
the traversal order. If the path from s to f does
not exist, print -1.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
4 4 1 3 1 2 1 2 3 2 3 4 5 4 1 4 |
3 1 2 3 |
SOLUTION
graphs – Dijkstra
algorithm
Algorithm analysis
To solve the
problem, it is necessary to implement Dijkstra’s algorithm. Given the restrictions on
the number of vertices and edges, the graph should be represented by an adjacency list.
Example
Sample graph has the form:
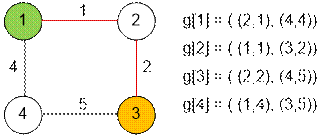
Algorithm realization
The graph is
stored in an adjacency list g, where g[i] contains a vector of pairs
(vertex j, edge length between i and j). Let’s declare
additional global arrays for Dijkstra’s algorithm:
·
dist[i] stores the shortest distance to the vertex i;
·
parent[i] stores the vertex number from which we arrived to i moving from the source
along the shortest path.
#define MAX 5010
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
int used[MAX], dist[MAX], parent[MAX];
vector<vector<pair<int, int> >
> g;
Function Relax relaxes
the edge (v, to)
with weight cost.
void Relax(int
v, int to, int
cost)
{
if (dist[to]
> dist[v] + cost)
{
dist[to] = dist[v] + cost;
parent[to] = v;
}
}
Function Find_Min
searches for the vertex with the smallest distance dist[i]
from the source among those to which the shortest distance has not yet been
calculated (for which used[i] = 0).
int Find_Min(void)
{
int i, v, min
= INF;
for(i = 1; i
<= n; i++)
if
(!used[i] && (dist[i] < min)) min = dist[i], v = i;
if (min ==
INF) return -1;
return v;
}
Function path
prints the shortest path from the
source to the vertex v.
For this, we use parent array.
void path(int
v)
{
if (v == -1) return;
path(parent[v]);
if (parent[v]
!= -1) printf(" ");
printf("%d",v);
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data. Construct an adjacency
list g of the graph.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
scanf("%d %d",&s,&f);
g.resize(n+1);
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d
%d",&b,&e,&w);
g[b].push_back(make_pair(e,w));
g[e].push_back(make_pair(b,w));
}
Initialization of global arrays. The
distance from source to source (dist[s]) is set to 0.
memset(dist,0x3F,sizeof(dist));
dist[s] = 0;
memset(parent,-1,sizeof(parent));
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
Start the cycle of Dijkstra’s algorithm. Since the graph contains n vertices, it
is enough to perform n – 1 iterations.
for(i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
v = Find_Min();
If no vertex can be included into the set of vertices to which the shortest distance is
already calculated, then end the algorithm.
if (v == -1) break;
Relax all the edges outgoing from the
vertex v.
for(j = 0; j
< g[v].size(); j++)
{
to = g[v][j].first;
cost = g[v][j].second;
if
(!used[to]) Relax(v,to,cost);
}
The shortest distance to v is
already computed (it is
in dist[v]).
used[v] = 1;
}
Print the answer depending on the value
of dist[f]. If it equals to infinity,
then there is no path to the required vertex. Otherwise, print the required shortest distance and shortest path.
if (dist[f] == INF)
printf("-1\n");
else
{
printf("%d\n",dist[f]);
path(f); printf("\n");
}
Algorithm realization – priority queue, adjacency list
Implement Dijkstra’s algorithm using a priority queue and adjacency list.
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#define MAX 2010
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
using namespace
std;
int i, j, v, d, to, cost, n, m, s, f, b,
e, w;
int used[MAX], dist[MAX], parent[MAX];
vector<vector<pair<int, int> >
> g;
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,
vector<pair<int,int>
>,
greater<pair<int,int> > >
pq; //(distance,node)
void Relax(int
v, int to, int
cost)
{
if (dist[to]
> dist[v] + cost)
{
dist[to] = dist[v] + cost;
pq.push(make_pair(dist[to],to));
parent[to] = v;
}
}
void path(int
v)
{
if (v == -1) return;
path(parent[v]);
if (parent[v]
!= -1) printf(" ");
printf("%d",v);
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&n,&m);
scanf("%d
%d",&s,&f);
g.resize(n+1);
for(i = 0; i
< m; i++)
{
scanf("%d
%d %d",&b,&e,&w);
g[b].push_back(make_pair(e,w));
g[e].push_back(make_pair(b,w));
}
memset(dist,0x3F,sizeof(dist));
dist[s] = 0;
memset(parent,-1,sizeof(parent));
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
pq.push(make_pair(0,s));
while(!pq.empty())
{
v = pq.top().second; d = pq.top().first;
pq.pop();
if (d >
dist[v]) continue;
for(j = 0; j < g[v].size(); j++)
{
to = g[v][j].first;
cost = g[v][j].second;
if
(!used[to]) Relax(v,to,cost);
}
used[v] = 1;
}
if (dist[f]
== INF)
printf("-1\n");
else
{
printf("%d\n",dist[f]);
path(f); printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Algorithm realization – priority queue,
adjacency list, pair structure
Implement Dijkstra’s algorithm using a priority queue with adjacency list
using own structure (vertex, distance).
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#define MAX 2010
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
using namespace
std;
int i, j, v, d, to, cost, n, m, s, f, b,
e, w;
int used[MAX], dist[MAX], parent[MAX];
struct edge
{
int node,
dist;
edge(int
node, int dist) : node(node), dist(dist) {}
};
bool operator<
(edge a, edge b)
{
return a.dist
> b.dist;
}
vector<vector<edge>
> g;
priority_queue<edge>
pq;
void Relax(int
v, int to, int
cost)
{
if (dist[to]
> dist[v] + cost)
{
dist[to] = dist[v] + cost;
pq.push(edge(to,dist[to]));
parent[to] = v;
}
}
void path(int
v)
{
if (v == -1) return;
path(parent[v]);
if (parent[v]
!= -1) printf(" ");
printf("%d",v);
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&n,&m);
scanf("%d
%d",&s,&f);
g.resize(n+1);
for(i = 0; i
< m; i++)
{
scanf("%d
%d %d",&b,&e,&w);
g[b].push_back(edge(e,w));
g[e].push_back(edge(b,w));
}
memset(dist,0x3F,sizeof(dist));
dist[s] = 0;
memset(parent,-1,sizeof(parent));
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
pq.push(edge(s,0));
while(!pq.empty())
{
edge e = pq.top(); pq.pop();
v = e.node;
if (e.dist
> dist[v]) continue;
for(j = 0;
j < g[v].size(); j++)
{
to = g[v][j].node;
cost = g[v][j].dist;
if
(!used[to]) Relax(v,to,cost);
}
used[v] = 1;
}
if (dist[f]
== INF)
printf("-1\n");
else
{
printf("%d\n",dist[f]);
path(f); printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Algorithm realization – adjacency matrix
Implement Dijkstra’s algorithm using the adjacency matrix.
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#define MAX 2001
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
using namespace std;
int i, j, mn, n, m, s, f;
int b, e, len, v;
int g[MAX][MAX],
used[MAX], dist[MAX], parent[MAX];
void PrintPath(int v)
{
vector<int>
res;
while (v !=
-1)
{
res.push_back(v);
v = parent[v];
}
for (int i =
res.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
printf("%d
", res[i]);
printf("\n");
}
void Relax(int i, int j)
{
if (dist[i] +
g[i][j] < dist[j])
{
dist[j] =
dist[i] + g[i][j];
parent[j] = i;
}
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d
%d", &n, &m);
scanf("%d
%d", &s, &f);
memset(g, 0x3F, sizeof(g));
memset(used, 0, sizeof(used));
for (i = 1; i <=
m; i++)
{
scanf("%d
%d %d", &b, &e, &len);
g[b][e] = g[e][b] = len;
}
memset(dist, 0x3F, sizeof(dist));
dist[s] = 0;
memset(parent, -1, sizeof(parent));
for (i = 1; i <
n; i++)
{
mn = INF; v =
-1;
for (j =
1; j <= n; j++)
if
(!used[j] && dist[j] < mn) { mn = dist[j]; v = j; }
if (v
== -1) break;
for (j =
1; j <= n; j++)
if
(used[j] == 0 && g[v][j] != INF) Relax(v, j);
used[v] = 1;
}
if (dist[f] == INF)
printf("-1\n");
else
{
printf("%d\n",
dist[f]);
PrintPath(f);
}
return 0;
}
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int g[][],
used[], dist[], parent[];
static final int INFINITY =
1000000000;
static void
PrintPath(int v)
{
if (v ==
-1) return;
PrintPath(parent[v]);
System.out.print(v + "
");
}
static void
Relax(int i, int j)
{
if (dist[i] + g[i][j]
< dist[j])
{
dist[j] = dist[i] + g[i][j];
parent[j] = i;
}
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int m = con.nextInt();
int s = con.nextInt();
int f = con.nextInt();
used = new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(used, 0);
g = new int[n+1][n+1];
for (int[] row: g)
Arrays.fill(row, INFINITY);
for(int i = 1;
i <= m; i++)
{
int b = con.nextInt();
int e = con.nextInt();
int distance = con.nextInt();
g[b][e] = g[e][b] = distance;
}
dist = new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(dist, INFINITY);
dist[s] =
0;
parent = new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(parent,
-1);
for(int i = 1;
i < n; i++)
{
int min = INFINITY, v =
-1;
for(int j = 1;
j <= n; j++)
if (used[j] ==
0 && dist[j]
< min) {min = dist[j]; v = j;}
if (v ==
-1) break;
for(int j = 1;
j <= n; j++)
if (used[j] ==
0 && g[v][j] != INFINITY) Relax(v, j);
used[v] =
1;
}
if (dist[f] == INFINITY)
System.out.println("-1");
else
{
System.out.println(dist[f]);
PrintPath(f);
System.out.println();
}
con.close();
}
}