5084. Interval less query
Given an array of size n, answer q
queries of the next kind: how many numbers on interval [l, r] have value less than x.
Input. The first line contains the size n (1 ≤ n
≤ 105) of array. The next line
contains n integers. Number of queries q (1 ≤ q ≤ 105) is given
in the next line. Each of the next q lines contains one query: three
integers l, r and x (l ≤ r, 1
≤ x ≤ 109).
Output. For each query print in a separate line how many
numbers on interval [l, r]
have value less than x.
|
Sample
input |
Sample output |
|
8 1 3 2 4 3 10
5 5 4 1 8 5 1 4 3 5 8 9 2 6 4 |
5 2 3 3 |
SOLUTION
segment tree
Algorithm analysis
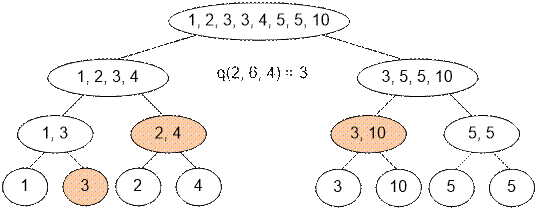
Let’s create an
additional array at each vertex of the segment tree. The vertex corresponding
to the fundamental segment [i; j], contains in its array a sorted set of numbers ai, …, aj. The time to build such a
tree is O(nlog2n).
To find the
number of integers from the segment [l, r] that are less than x, this interval should be divided into a set of
fundamental segments and a
binary search should be performed in each of them, counting the number of
elements less than x. The query time is ![]() .
.
Example
Algorithm realization
Declare a segment
tree. Each of its
vertices stores an array of integers.
vector<vector<int> > SegTree;
Input
numbers are stored in the array a.
vector<int> a;
The
function BuildTree builds a segment tree from array a. The sorted array at each vertex
is obtained by merging the arrays of its children in O(n) using the merge
function.
void BuildTree(int v, int lpos, int rpos)
{
if (lpos == rpos)
SegTree[v].push_back(a[lpos]);
else
{
int mid = (lpos + rpos) / 2;
BuildTree(2*v, lpos, mid);
BuildTree(2*v+1, mid+1, rpos);
SegTree[v].resize(rpos - lpos + 1);
merge(SegTree[2*v].begin(), SegTree[2*v].end(),
SegTree[2*v+1].begin(),
SegTree[2*v+1].end(),
SegTree[v].begin());
}
}
The function Query counts the
number of integers in the
interval [l, r] that are less than x. For each fundamental segment [left; right] using the
function lower_bound find the number of numbers less than x.
int Query(int v, int lpos, int rpos, int left, int right, int x)
{
if (left > right) return 0;
if ((lpos == left) && (rpos == right))
return
lower_bound(SegTree[v].begin(),
SegTree[v].end(), x) –
SegTree[v].begin();
int mid = (lpos + rpos) / 2;
return Query(2*v, lpos, mid, left, min(mid, right), x) +
Query(2*v+1, mid+1, rpos, max(left, mid+1), right, x);
}
The main part of the program. Read the input array of integers.
scanf("%d",&n);
a.resize(n + 1);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
Build a segment tree from array a.
SegTree.resize(4*n);
build(1,1,n);
Sequentially process q queries.
scanf("%d",&q);
for(i = 0; i < q; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d
%d",&l,&r,&x);
printf("%d\n",Query(1,1,n,l,r,x));
}
Algorithm realization – SQRT decomposition
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
vector<int>
a;
vector<vector<int>
> b;
int i, n, q, len, blocks, l,
r, x;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",
&n);
a.resize(n);
len
= sqrt(n) + 1;
blocks = ceil((double)n / len);
b.resize(len);
for (i = 0;i <
n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",
&a[i]);
b[i / len].push_back(a[i]);
}
scanf("%d",
&q);
for (i = 0;i <
blocks; i++)
sort(b[i].begin(),
b[i].end());
while
(q--)
{
scanf("%d
%d %d", &l, &r, &x);
l--; r--;
int res
= 0;
int c_l = l / len, c_r = r / len;
if (c_l == c_r)
{
for (i =
l; i <= r; i++)
if (a[i] <
x) res++;
}
else
{
for (i =
l; i <= (c_l + 1)*len -
1; i++)
if (a[i] <
x) res++;
for (i =
c_l + 1; i <= c_r - 1;
i++)
res += lower_bound(b[i].begin(),
b[i].end(), x) - b[i].begin();
for (i =
c_r * len; i <= r; i++)
if (a[i] <
x) res++;
}
printf("%d\n",
res);
}
return 0;
}