5190. Construct a triangle with two sides and the included
angle
Construct a triangle given
two sides and included angle.
Input.
Contains three real numbers – the lengths of two sides of triangle and the
angle between them in degrees. The lengths of the sides are positive numbers
not exceeding 104, the angle is a positive number less
than 180.
Output. Print 6 real numbers – the coordinates of the vertices of any triangle
corresponding to the given input data with an accuracy at
least 6 decimal digits.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
10 5 60 |
0 0 10.0 0 2.5000000000 4.3301270189 |
SOLUTION
geometry
Algorithm analysis
Let A, B, C be three vertices of triangle, BC = a, AC = b. Place the
origin of the coordinate system (0, 0) at point C, direct the abscissa
axis along the vector CB. Then point B has coordinates (a, 0).
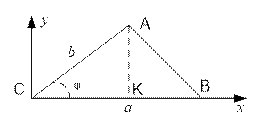
Draw the height AK. From tringle CAK: AK = AC
sin φ,
CK = AC cos φ. Considering that AC = b, point À will
have coordinates (b cos φ, b sin φ).
Algorithm realization
Declare the constant π.
#define PI acos(-1.0)
Read the input data.
scanf("%lf
%lf %lf",&a,&b,&fi);
Convert angle fi to radians.
fi = fi / 180 * PI;
Print the coordinates of three points.
printf("%.6lf
%.6lf\n",0,0);
printf("%.6lf
%.6lf\n",a,0);
printf("%.6lf
%.6lf\n",b*cos(fi),b*sin(fi));
Java
realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static double[] kramer(double a1, double b1, double c1,
double a2, double b2, double c2)
{
double res[] = new double[2]; // x, y
double d = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1;
double dx = c1 * b2 - c2 * b1;
double dy = a1 * c2 - a2 * c1;
res[0] = dx / d;
res[1] = dy / d;
return res;
}
public static void
main(String []args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
double a = con.nextDouble();
double b = con.nextDouble();
double fi = con.nextDouble();
fi = fi / 180 * Math.PI;
System.out.println("0 0");
System.out.println(a + " " + 0);
System.out.println(b *
Math.cos(fi) + " " + b * Math.sin(fi));
con.close();
}
}