5329. Party
How many ways are there to choose k
out of n participants in the summer math camp, each of whom will receive
kefir? Print
the answer modulo 9929.
Input. Two integers n and k (0 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 500).
Output. Print the number of ways modulo 9929.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
6 3 |
20 |
SOLUTION
combinatorics – binomial
coefficient
Algorithm analysis
The answer to
the problem will
be the value of ![]() . Since we need to find the binomial coefficient by modulo, we’ll try to avoid division
during calculations. To achieve this, use the relation:
. Since we need to find the binomial coefficient by modulo, we’ll try to avoid division
during calculations. To achieve this, use the relation: ![]() =
= ![]() +
+ ![]() ,
, ![]() = 1.
= 1.
The problem can
also be solved using the formula:
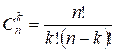 =
= ![]() =
= ![]() ,
,
by replacing
division with multiplication by the inverse number modulo 9929.
Note that the
number 9929 is a prime. That is, n / i = n * (i-1) mod 9929.
According to Fermat’s theorem, i9928 mod 9929 = 1 or (i * i9927) mod 9929 = 1, hence the inverse of i modulo 9929 will be i9927 mod 9929. Thus,
(i-1) mod 9929 = i9927 mod 9929
Algorithm implementation
Declare the constants and array cnk, where cnk[n][k]
= ![]() .
.
#define MAX 510
#define MOD 9929
int cnk[MAX][MAX];
The c function computes the value of the binomial coefficient ![]() .
.
int c(int
n, int k)
{
if (cnk[n][k]
> 0) return cnk[n][k];
if (n - k
< k) return c(n,n-k);
if (!k) return cnk[n][k] = 1;
return
cnk[n][k] = (c(n-1,k) + c(n-1,k-1)) % MOD;
}
The main part of the program. Initialize the cnk array with zeros. Read the input data.
memset(cnk,0,sizeof(cnk));
scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);
Compute and print the answer.
printf("%d\n",c(n,k));
Algorithm implementation – loops
Declare the constants and array cnk, where cnk[n][k]
= ![]() .
.
#define MAX 502
#define MOD 9929
int cnk[MAX][MAX];
The FillCnk function fills the cnk array with
binomial coefficients.
void FillCnk(void)
{
int n, k;
memset(cnk,0,sizeof(cnk));
Initialize cnk[n][0] = ![]() = 1.
= 1.
for(n = 0; n
< MAX; n++) cnk[n][0] = 1;
Perform the computation using the formula ![]() =
= ![]() +
+ ![]() modulo MOD.
modulo MOD.
for(n = 1; n
< MAX; n++)
for(k = 1; k
<= MAX; k++)
cnk[n][k] = (cnk[n-1][k] + cnk[n-1][k-1]) %
MOD;
}
The main part of the program. Fill
the array of binomial coefficients.
FillCnk();
Read the input data. Compute
and print the
answer.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);
printf("%d\n",cnk[n][k]);
Algorithm implementation – inverse modulo
The pow function computes xn
mod p.
int pow(int x, int n, int p)
{
if (n ==
0) return 1;
if (n % 2
== 0) return pow((x * x) % p, n / 2,
p);
return (x *
pow(x, n - 1, p)) % p;
}
The inverse function computes the number that
is the inverse of x modulo p: x-1
mod p (where p is prime).
int inverse(int x, int p)
{
return pow(x, p - 2,
p);
}
The Cnk function computes the
value of the binomial coefficient ![]() modulo p. To achieve this, rewrite an
expression
modulo p. To achieve this, rewrite an
expression
res = res * (n – i
+ 1) / i
in the form
res = (res * (n – i
+ 1) * (i-1
mod p)) mod
p
int Cnk(int n, int k, int p)
{
int res
= 1;
if (k >
n - k) k = n - k;
for (int i =
1; i <= k; i++)
res =
((res * (n - i + 1)) % p * inverse(i, p)) % p;
return res;
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d",
&n, &k);
Compute and print the answer.
res = Cnk(n, k, 9929);
printf("%d\n",
res);
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int dp[][];
static int MOD =
9929;
static int Cnk(int n, int k)
{
if (n == k) return 1;
if (k ==
0) return 1;
if (dp[n][k] !=
-1) return dp[n][k];
return dp[n][k] = (Cnk(n - 1,
k - 1) + Cnk(n - 1,
k)) % MOD;
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int k = con.nextInt();
dp = new int[n+1][k+1];
for(int i = 0;
i <= n; i++)
Arrays.fill(dp[i],-1);
int res = Cnk(n,k);
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Java implementation – loops, long arithmetic
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
public class Main
{
static
BigInteger Cnk(int n, int k)
{
BigInteger res = BigInteger.ONE;
BigInteger MOD = BigInteger.valueOf(9929);
BigInteger p = BigInteger.valueOf(n);
BigInteger q = BigInteger.valueOf(1);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
res = res.multiply(p).multiply(q.modInverse(MOD)).mod(MOD);
p = p.subtract(BigInteger.ONE);
q = q.add(BigInteger.ONE);
}
return res;
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int k = con.nextInt();
BigInteger
res = Cnk(n,k);
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
The Cnk function computes the
value of the binomial coefficient ![]() and memoizes its value in the cell
dp[n][k].
and memoizes its value in the cell
dp[n][k].
def Cnk(n, k, dp):
if n == k: return 1
if k == 0: return 1
if dp[n][k] != -1: return dp[n][k]
dp[n][k] = (Cnk(n - 1, k - 1, dp) +
Cnk(n - 1, k, dp)) % 9929
return dp[n][k]
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
n, k = map(int, input().split())
Initialize
a two-dimensional list for memoizing the values:
dp[x][y] = ![]()
dp = [[-1] * 501 for _ in range(501)]
Compute and print the answer.
print(Cnk(n, k, dp))