5854. Maximum sum basic
A rectangular
table of size n rows by m columns is given.
Each cell of this table contains one integer. You can traverse the table from
top to bottom, starting from any cell in the top row, and at each step, move to
one of the “lower neighboring” cells. In other words, from a cell with coordinates (i,
j), you can move to (i + 1, j – 1), (i + 1, j), or (i + 1, j + 1). If j = m, the last of the
three movement options is not possible. If j = 1, the first option is not possible. The route ends in one of
the cells of the bottom row.
Write a program
that finds the maximum possible sum of values of cells passed along any valid
path.
Input. The first line
contains n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 200) – the number of
rows and columns. Each of the next n lines contains m integers
(with absolute values not exceeding 106) – the values of the
cells in the table.
Output. Print one single
integer – the maximum possible sum.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
4 3 1 15 2 9 7 5 9 2 4 6 9 -1 |
42 |
SOLUTION
dynamic programming
Algorithm analysis
Let a[i][j] be the input table. Let dp[i][j] represent the
maximum sum of numbers along a path from any cell in the first row to the cell (i, j). Then
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i – 1][j – 1], dp[i – 1][j], dp[i – 1][j + 1]) + a[i][j]
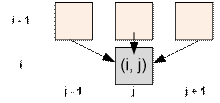
To correctly calculate the
values in the first and last columns, set
dp[i][0] = dp[i][m + 1] = -∞
Initialize the first row
of the dp array with the values from the first row of the table à:
dp[1][i] = a[1][i], 1 ≤ i ≤ m
The answer to
the problem will be the maximum value in the last (n-th)
row of the dp array.
Example
Consider the input example.
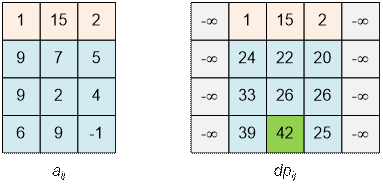
Algorithm implementation
Declare a
constant MIN to store the minimum value, as well as arrays a
and dp.
#define MAX 202
#define MIN
-2000000000
int a[MAX][MAX],
dp[MAX][MAX];
Read the
input data. The top-left corner of the table will be stored in a[1][1].
Fill the columns with indices 0 and m
+ 1 in the dp array with the minimum possible value MIN.
scanf("%d %d",
&n, &m);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
dp[i][0] =
dp[i][m + 1] = MIN;
for (j =
1; j <= m; j++)
scanf("%d",
&a[i][j]);
}
Copy the
first row of array a into the array dp.
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
dp[1][i] =
a[1][i];
Recalculate
the maximum sums along paths from the top row to the cell (i, j) and store them
in the array dp.
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= m; j++)
dp[i][j] = max(max(dp[i -
1][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]),
dp[i - 1][j + 1]) + a[i][j];
Find the
largest number in the last (n-th) row of the dp array.
res = MIN;
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if (dp[n][i]
> res) res = dp[n][i];
Print the
answer.
printf("%d\n",
res);
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int a[][], dp[][];
final static int MIN = -2000000000;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int m = con.nextInt();
dp = new int[n+1][m+2];
a = new int[n+1][m+2];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
dp[i][0] = dp[i][m + 1] = MIN;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
a[i][j] = con.nextInt();;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
dp[1][i] = a[1][i];
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
dp[i][j] = Math.max(Math.max(dp[i - 1][j - 1], dp[i - 1][j]), dp[i - 1][j + 1]) + a[i][j];
int res = MIN;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if (dp[n][i] > res) res = dp[n][i];
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}