7311. Insert Parentheses
Milhouse need to
solve a school task by tomorrow and needs your help. Here is the task:
Given a string
of parentheses, you must turn it into a well formed string by inserting as few
parentheses as possible, at any position (you cannot delete or change any of
the existing parentheses). A well-formed string of parentheses is defined by
the following rules:
·
The empty string is well formed.
·
If s
is a well formed string, (s) is a
well formed string.
·
If s
and t are well formed strings, their
concatenation st is a well formed
string.
As examples,
"(()())", "" and "(())()" are well formed strings
and "())(", "()(" and ")" are malformed strings.
Input. Given a
string of parentheses, it contains between 1 and 50 characters, inclusive.
Output. Print
the minimum number of parentheses that need to be inserted to make the input
string into a well formed string.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
(()(() |
2 |
SOLUTION
stack
Algorithm analysis
Use the counter balance, to
calculate the balance of open and closed parentheses. Once balance becomes
negative, one extra opening
parenthesis must be inserted in order for the processed string prefix to
become correct.
At the end of processing
a string, you
must add balance closing brackets.
Example
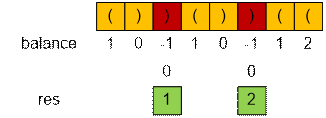
For the input
string to be correct, you need to add balance
+ res = 2 + 2 = 4 brackets.
Algorithm realization
In the variable res count
the number of times the
variable balance becomes negative.
balance = res = 0;
while(scanf("%c",&c), c != '\n')
{
Calculate
the balance of the brackets. Handle the case when it becomes negative.
balance += (c == '(') ? 1 : -1;
if (balance < 0)
{
res++;
balance = 0;
}
}
Print
the answer.
printf("%d\n",res
+ balance);
Java realization – symbol array
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
char[] s = con.nextLine().toCharArray();
int balance = 0, res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length; i++)
{
balance += (s[i] == '(') ? 1 : -1;
if (balance <
0)
{
res++;
balance = 0;
}
}
System.out.println(res + balance);
con.close();
}
}
Java realization – string
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = con.nextLine();
int balance = 0, res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
{
balance += (s.charAt(i) == '(') ? 1 : -1;
if (balance < 0)
{
res++;
balance = 0;
}
}
System.out.println(res + balance);
con.close();
}
}