7447. Cut a string
Given a string s. You are allowed to choose any two
identical adjacent characters and delete them from the string. This operation
can be repeated as long as it is possible.
Before performing
this operation, you may delete any number of characters from the string.
Determine the
minimum number of characters that must be deleted beforehand so that
afterwards, by applying the allowed operation, you can obtain an empty string.
Input. One string s (1 ≤ |s|
≤ 100).
Output. Print the
minimum number of characters that must be deleted beforehand.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
abacdeec |
2 |
SOLUTION
dynamic programming
Algorithm analysis
Let dp[l][r]
= f(l, r)
be the
minimum number of characters that need to be deleted from the substring sl … sr so that, by performing the
allowed operations (removing two identical adjacent characters), we can obtain
an empty string. Then:
·
f(l, r) = 0, if l > r;
·
f(l, l) = 1, since the single character must be
deleted in advance;
·
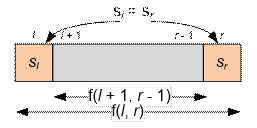
f(l, r) = f(l
+ 1, r – 1), if s[l]
= s[r]. In this case, the inner part of the
substring is deleted first, after which the boundary characters become adjacent
and can be removed;
·
f(l, r) = 1 + f(l
+ 1, r), if the first character is deleted;
·
f(l, r) = 1 + f(l,
r – 1), if the last character is deleted;
However, both of these
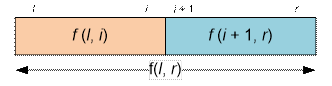
cases can be conveniently generalized as follows: to solve the problem on the
segment [l; r], split it into two subsegments [l;
i] and [i + 1; r] (l ≤ i < r) and choose the minimum value:
f(l, r)
= ![]()
For example:
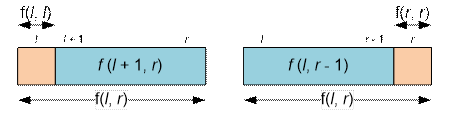
·
deleting the first character is equivalent to choosing i = l (f(l, l)
= 1);
·
deleting the last character is equivalent to choosing i = r – 1 (f(r, r)
= 1)
The answer to the problem
will be dp[0][n – 1] = f(0, n – 1), where n is the length of the
input string.
Example
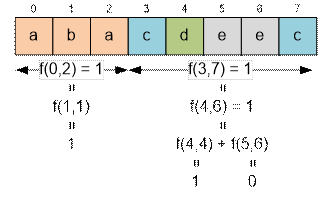
Let’s consider the example
given in the problem statement. We have:
f(0, 7) = f(0, 2) + f(3,
7) = 1 + 1 = 2
Algorithm implementation
Let's declare the constants and the array.
#define MAX 101
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
int dp[MAX][MAX];
The function f solves the problem on the segment [l; r].
int f(int l, int r)
{
if (l > r)
return 0;
if (l == r) return 1;
if (dp[l][r]
!= INF) return dp[l][r];
int &res = dp[l][r];
if (s[l] ==
s[r])
res = min(res, f(l + 1, r - 1));
for (int i = l; i < r; i++)
res = min(res, f(l, i) + f(i + 1, r));
return res;
}
The main part of the program. Read the input string.
cin >> s;
memset(dp,0x3F,sizeof(dp));
Compute and print the result f(0, n
– 1), where n is the length of the string s.
printf("%d\n",f(0, s.size() -
1));
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static String s;
static int dp[][];
static int f(int l, int r)
{
if (l > r) return 0;
if (l == r) return 1;
if (dp[l][r] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) return dp[l][r];
int res = dp[l][r];
if (s.charAt(l) == s.charAt(r))
res = Math.min(res, f(l + 1, r - 1));
for (int i = l; i < r; i++)
res = Math.min(res, f(l, i) + f(i + 1, r));
return dp[l][r] = res;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
s = con.nextLine();
int n = s.length();
dp = new int[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
dp[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println(f(0, n - 1));
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
Declare the constant INF.
INF = float('inf')
The function f solves the problem on the segment [l; r].
def f(l, r):
if l > r: return 0
if l == r: return 1
if dp[l][r] != INF:
return dp[l][r]
res = dp[l][r]
if s[l] == s[r]:
res = min(res, f(l + 1, r - 1))
for i in range(l, r):
res = min(res, f(l, i) + f(i + 1, r))
dp[l][r] = res
return res
The main part of the program. Read the input string s and compute
its length n.
s = input()
n = len(s)
Initialize the list dp.
dp = [[INF] * n for _ in
range(n)]
Compute and print the result f(0, n
– 1).
print(f(0, n - 1))