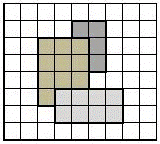
7504. Three rectangles
Three rectangles are painted on the white
sheet of paper so that their sides lie on the grid lines and the vertices have
integer coordinates. Find the total number of painted cells.
Input. Three lines contain four integers – the coordinates
of two opposite vertices of each rectangle (the coordinates do not exceed 100 by
absolute value).
Output. Print the number of painted cells.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
2 2 5 6 3 3 7 1 6 4 4 7 |
22 |
SOLUTION
two-dimensional array
Algorithm analysis
The coordinates
of the rectangle vertices do not
exceed 100 by
absolute value. Therefore, they take values from -100 to 100. Let’s shift the coordinates by the vector (100, 100) so that all values become non-negative
(now they vary from 0 to 200).
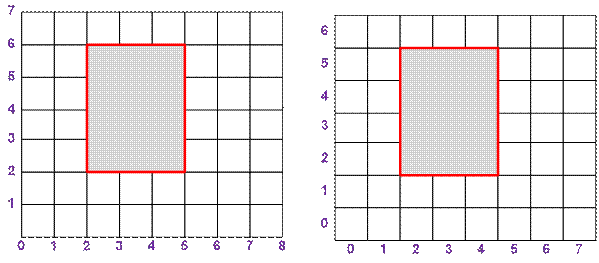
The coordinates
of the vertices in the input data are located in the grid nodes. Let’s number the
cells vertically and horizontally, starting from 0. Then the rectangle at the
grid nodes (a, b) – (c, d) will correspond
to the rectangle (a, b) – (c – 1, d – 1) on the cells.
For example, the
rectangle (2, 2) – (5, 6) at the grid nodes corresponds to the rectangle (2, 2)
– (4, 5) at the cells.
Declare a
two-dimensional array m[201][201]. Set element m[i][j] = 1 if one of the
input rectangles covers cell (i, j). After processing all three rectangles, count the number
of covered cells.
Algorithm realization
Declare the arrays.
#define MAX 210
int m[MAX][MAX];
The function swap swaps the numbers a and b.
void swap(int& a, int& b)
{
int temp = a; a = b; b = temp;
}
The main part of the program. Set all elements of array m to 0.
memset(m, 0, sizeof(m));
Sequentially process three rectangles.
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
Read the coordinates of the next rectangle (a, b) – (c,
d).
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &a,
&b, &c, &d);
Swap the coordinates so that (a, b) becomes the lower left corner, and (c, d) the upper
right. After this we will have a < c and b < d.
if (a > c) swap(a, c);
if (b > d) swap(b, d);
All cells that are covered by the rectangle (a, b) – (c – 1, d – 1) we mark in the
array m with ones. We shift the coordinates of the vertices by the vector (MAX
/ 2, MAX / 2), where MAX is the size of array (array indices cannot be
negative).
for (j = a; j < c; j++)
for (k = b; k < d; k++)
m[j + MAX / 2][k + MAX / 2] = 1;
}
In the variable res
count the number of covered cells.
res = 0;
for (i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
for (j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
res += m[i][j];
Print the answer.
printf("%d\n",res);