7807. Happy sum
It is known that
the number is happy, if its decimal notation contains only fours and sevens.
For example, the
numbers 4, 7, 47, 7777 and 4744474 are happy.
Let S be the set of happy numbers, no less than a and no more
than b:
S = {n : a ≤ n ≤ b, n is happy}
Calculate the
remainder of dividing by 1234567891 the next sum:
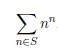
Input. Two integers a and b (1 ≤ a ≤ b ≤ 1018).
Output. Output the remainder of dividing the lucky sum
by 1234567891.
Explanation.
44 + 77 = 823799.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
1 10 |
823799 |
SOLUTION
complete
search +
exponentiation
Algorithm analysis
The modulus p = 1234567891 is prime. So, np – 1 = 1 (mod p). We have
nn (mod p) = (n mod p) (p – 1) + … + (p
– 1) + (n mod (p – 1)) (mod p) =
(n mod p) n mod (p – 1) (mod p)
For example 2323 (mod 5) = (23 mod 5) 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 3 (mod 5) = 33 (mod 5), because 34 (mod 5) = 1.
Let modPow(a, n) = an
mod p. Since n ≤ 1018, then the arguments of modPow(n, n) will have type long long and when
multiplying we get overflow. From the above equality we have:
modPow(n, n) = modPow(n mod p, n mod (p – 1))
Now we can pass int arguments to the function modPow.
To
generate happy numbers,
it should be noted that if n is happy, then numbers 10*n + 4 and 10*n + 7 will be also happy.
Algorithm realization
Define the module MOD = 1234567891.
#define MOD 1234567891
Function modPow returns the value of an mod MOD.
long long modPow(long long a, long long n)
{
if (n == 0) return 1;
if (n % 2 == 0) return modPow((a * a) % MOD, n / 2);
return (modPow(a, n - 1) * a) % MOD;
}
Recursive generation of happy numbers.
void f(long long n)
{
As soon as the next generated number n becomes greater than b, we stop to generate the numbers.
if (n > b) return;
Sum up the values nn only for those happy numbers n, for which a ≤ n ≤ b.
if (n >= a) res = (res + modPow(n % MOD, n % (MOD - 1))) % MOD;
In n is a
happy number, then numbers 10*n + 4 and 10*n + 7 will be
also happy.
f(n * 10 + 4);
f(n * 10 + 7);
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data.
scanf("%lld %lld", &a, &b);
res
= 0;
Generate the happy numbers
starting from 0. Calculate the required sum in the res variable.
f(0);
Print the answer.
printf("%lld\n", res);