8546. Find the sum
For the given value of n, compute
the sum
S = 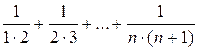
Input. One positive integer n (n ≤ 1000).
Output. Print the sum with 6 decimal places.
|
Sample input 1 |
Sample output 1 |
|
5 |
0.833333 |
|
|
|
|
Sample input 2 |
Sample output 2 |
|
12 |
0.923077 |
SOLUTION
loops
Algorithm analysis
Compute the specified sum
using a loop.
Let’s calculate the specified sum mathematically:
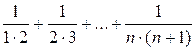 =
= 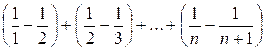 =
= ![]()
Now we can use this formula
to find the answer.
Algorithm implementation
Read the input value of n.
scanf("%d",&n);
In the variable i, iterate through
the numbers 1, 2, 3, … n. On each iteration, add the value of 1 / (i * (i + 1)) to the
resulting sum s.
s = 0; i = 1;
while(i <= n)
{
s += 1.0 / i / (i+1);
i++;
}
Print the answer.
printf("%lf\n",s);
Algorithm implementation– for loop
Read the input value of n.
scanf("%d",&n);
Compute the desired sum in the
variable s.
s = 0;
Using a for
loop, compute the sum of n terms. The i-th term is equal to 1 / (i * (i + 1)).
for
(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
s += 1.0 / (i *
(i+1));
Print the answer.
printf("%.6lf\n",s);
Algorithm implementation– formula
Read the input value of n.
scanf("%d", &n);
Compute the answer using the formula and print it.
s = 1 - 1.0 / (n + 1);
printf("%.6lf\n", s);
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
double s = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
s += 1.0 / (i * (i+1));
System.out.printf("%6f\n", s);
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
Read the input value of n.
n = int(input())
Compute the desired sum in the
variable s.
s = 0;
Using a for
loop, compute the sum of n terms. The i-th term is equal to 1 / (i * (i + 1)).
for i in range(1, n+1):
s += 1.0 / (i * (i + 1));
Print the answer.
print(s)