8760. Depth first search
The undirected graph is given. Start a depth-first search from the given
vertex v and print the vertex numbers in the order of their
first visit.
Input. The first line contains the number of vertices n (n ≤ 100) and
edges m of the graph. Each of the following
m lines contains two vertices a and b – an undirected edge of the graph. The last line contains the
vertex v.
Output. Start a depth-first search from vertex v and print the vertex
numbers in the order of their first visit.
|
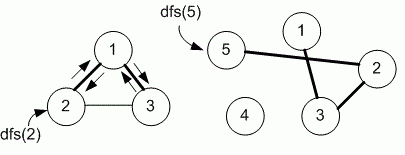
Sample input 1 |
Sample output 1 |
|
3 3 1 2 2 3 1 3 2 |
2 1 3 |
|
|
|
|
Sample input 2 |
Sample output 2 |
|
5 3 1 3 2 3 2 5 5 |
5 2 3 1 |
SOLUTION
graphs – depth first search
Algorithm analysis
Let’s build an adjacency matrix from the list
of edges. Start a
depth-first search from the specified vertex v. Each time we enter a new vertex, we print its number.
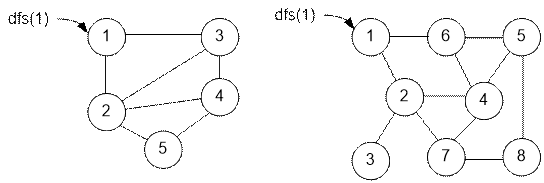
Exercise
Solve the problem for the next graphs:
Algorithm realization – adjacency matrix
Declare an adjacency matrix g and an array used.
#define MAX 101
int g[MAX][MAX], used[MAX];
The dfs function performs a depth-first
search from vertex v.
void dfs(int v)
{
Print the vertex v.
printf("%d ", v);
Mark the vertex v as visited.
used[v] = 1;
Iterate
over the vertices i, that can be reached from v. Moving
from v to i is possible if:
· There
is an edge (v, i), that is, g[v][i] = 1;
· The
vertex i is not visited (used[i] = 0)
If both conditions are true, we continue the
depth-first search from vertex i.
for (int i = 1; i <=
n; i++)
if ((g[v][i] == 1)
&& (used[i] == 0)) dfs(i);
}
The main part of the program. Read the number of vertices n and edges m in the
graph.
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
Initialize the arrays with
zeroes.
memset(g,
0, sizeof(g));
memset(used,
0, sizeof(used));
Read the list
of edges. Construct the adjacency
matrix.
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
g[a][b] = g[b][a] = 1;
}
Read vertex v and start a depth-first search from it.
scanf("%d", &v);
dfs(v);
printf("\n");
Algorithm realization – adjacency list
Declare an adjacency list g and an
array used.
vector<vector<int> > g;
vector<int> used;
The dfs function performs a depth-first
search from vertex v.
void dfs(int v)
{
Mark the vertex v as visited.
used[v] =
1;
Print the vertex v.
printf("%d ", v);
The array g[v] contains a list of vertices adjacent to v. Iterate over the vertices to that
can be reached from v.
for (int to : g[v])
Consider the edge (v, to). We can move
to vertex to from v if the vertex to is not visited (used[to] = 0).
if (used[to] == 0) dfs(to);
}
The main part of the program. Read the number of vertices n and edges m in the
graph.
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
Set the size of arrays g and used.
g.resize(n + 1);
used.resize(n
+ 1);
Read the list
of edges. Construct the adjacency
list.
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
Read vertex v and start a depth-first search from it.
scanf("%d", &v);
dfs(v);
printf("\n");
Java realization – adjacency matrix
import
java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int g[][], used[];
static int n, m;
static void
dfs(int v)
{
System.out.printf(v + " ");
used[v] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (g[v][i] == 1 && used[i] == 0) dfs(i);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
n = con.nextInt();
m = con.nextInt();
g = new int[n+1][n+1];
used = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a = con.nextInt();
int b = con.nextInt();
g[a][b] = g[b][a] = 1;
}
int v = con.nextInt();
dfs(v);
System.out.println();
}
}
Java realization – array of ArrayList
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static ArrayList<Integer>[] g;
static int used[];
static int n, m;
static void dfs(int v)
{
System.out.print(v + " ");
used[v] = 1;
for(int to : g[v])
if (used[to] == 0) dfs(to);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
n = con.nextInt();
m = con.nextInt();
g = new ArrayList[n+1]; // unchecked
used = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
g[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a = con.nextInt();
int b = con.nextInt();
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
int v = con.nextInt();
dfs(v);
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}
Java realization – ArrayList of ArrayList
import
java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> g;
static int used[];
static int n, m;
static void
dfs(int v)
{
System.out.printf(v + " ");
used[v] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < g.get(v).size(); i++)
{
int to = g.get(v).get(i);
if (used[to] == 0) dfs(to);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
n = con.nextInt();
m = con.nextInt();
g = new
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
used = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
g.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int a = con.nextInt();
int b = con.nextInt();
g.get(a).add(b);
g.get(b).add(a);
}
int v = con.nextInt();
dfs(v);
System.out.println();
con.close();
}
}
Python realization
The dfs function performs a depth-first
search from vertex v.
def dfs(v):
Print the vertex v.
print(v, end = ' ')
Mark the vertex v as visited.
used[v] = True
The list g[v] contains the numbers of vertices adjacent to v. Iterate over the vertices to that can be reached from v. It’s possible to go to vertex
to from v if vertex to is not visited (used[to] = 0).
for to in g[v]:
if not used[to]:
dfs(to)
The main
part of the program. Read the
number of vertices n and edges m in the
graph.
n, m = map(int, input().split())
Create the
adjacency list g and the list used.
g = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
used = [False] * (n + 1)
Read the list
of edges. Construct the adjacency list.
for _ in range(m):
a, b = map(int, input().split())
g[a].append(b)
g[b].append(a)
Read vertex v and start a depth-first search from it.
v = int(input())
dfs(v)