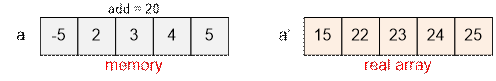853. Sereja and Array
Sereja has got an
array, consisting of n integers a1, a2, ..., an. Sereja is an active boy, so
he is now going to complete m operations.
Each operation will have one of the three forms:
·
Make vi-th array element
equal to xi. In other words,
perform the assignment avi = xi.
·
Increase each array element by yi. In other words, perform n assignments ai = ai +
yi (1 ≤ i ≤ n).
·
Take a piece of paper and write out the qi-th array element. That is, the element aqi.
Help Sereja,
complete all his operations.
Input. The first line contains integers n, m
(1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line
contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) – the original
array.
Next m lines describe operations, the i-th line describes the i-th operation. The first number in the i-th line is integer ti (1 ≤ ti ≤ 3), that represents
the operation type.
·
If ti
= 1, then it is followed by two integers vi and xi (1 ≤ vi ≤ n, 1 ≤ xi ≤ 109).
·
If ti
= 2, then it is followed by integer yi
(1 ≤ yi
≤ 104).
·
If ti
= 3, then it is followed by integer qi
(1 ≤ qi
≤ n).
Output. For each
third type operation print value aqi. Print the
values in the order, in which the corresponding queries follow in the input.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
5 6 1 2 3 4 5 3 1 2 10 1 1 5 3 1 2 10 3 1 |
1 5 15 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
10 11 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
8 9 10 3 2 3 9 2 10 3 1 3 10 1 1 10 2 10 2 10 3 1 3 10 3 9 |
2 9 11 20 30 40 39 |
SOLUTION
array processing
Algorithm analysis
Read the input
array a. Create a variable add, initialize it to zero. When performing an operation of the second type
(increasing each element of the array by yi), add add + = yi. Thus, in the absence of operations of the first type
(assignments avi = xi), the final state of the
element ai will be equal
to the initial state of ai
plus add. Then, to preserve the last
property in the case of the first operation, we must assign avi = xi – add.
Example
Let’s look at the
first example. Let ai be
the state of the array in memory, ai’ be the real state
of the array. Initial state of the array:
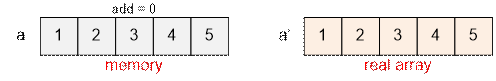
Since ai’ = ai + add, but initially add = 0, then ai’ = ai. That is,
initially physically each element of the array equals to itself.
Add 10 to all the
numbers in the array, add = add + 10 = 10. The following relation holds: ai’ = ai + add.
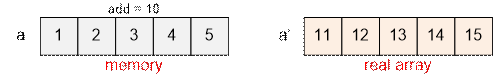
The next query: a1’ = 5.
Physically you should make the assignment
a1 = 5 – add,
after which the
array will take the form:
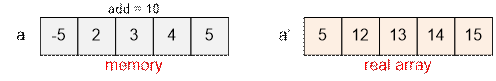
Next query is to print the first
element. We get a1’ = a1 + add = -5 + 10 = 5.
Again add 10 to all the
numbers of array: add = add + 10 = 20.
First element equals to a1’ = a1 + add = -5 + 20 = 15.
Algorithm realization
Declare an array a.
#define MAX 100010
int a[MAX];
Read the input array.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
Initialize the variable add.
add = 0;
Process m operations
sequentially. The type of operation read into the variable t.
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&t);
Carry out the assignment avi = xi
if (t == 1)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&v,&x);
a[v] = x - add;
} else
Increase each element of array by yi.
if (t == 2)
{
scanf("%d",&y);
add += y;
} else
Print the qi-th element of the array.
{
scanf("%d",&q);
printf("%d\n",a[q]
+ add);
}
}