9022. Count the triplets
Given three arrays
a, b and c, each consisting
of n integers. Find the number of triplets (ai,
bj, ck) such that the inequality ai < bj
< ck holds.
Input. The first line
contains the size of the arrays n (n ≤ 105).
The second line contains the elements of array a.
The third line contains the elements of array b.
The fourth line contains the elements of array c.
Output. Print the number of triplets (ai, bj,
ck) that satisfy the
condition ai < bj < ck.
Explanation. In the first test case, the valid triplets are (a1, b1, c1),
(a1, b2, c1), and (a1, b2, c2).
|
Sample input 1 |
Sample output 1 |
|
2 1 5 4 2 6 3 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
Sample input 2 |
Sample output 2 |
|
3 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 |
27 |
SOLUTION
binary search
Algorithm analysis
Let’s sort
all three arrays. For each element bj,
use binary search to determine:
·
the
number of elements x in array a that are less than bj,
·
the
number of elements y in array c that are greater than bj.
Then, for a
fixed value of bj, there
are exactly x * y triplets of the
form (ai, bj, ck) that satisfy the inequality ai < bj
< ck.
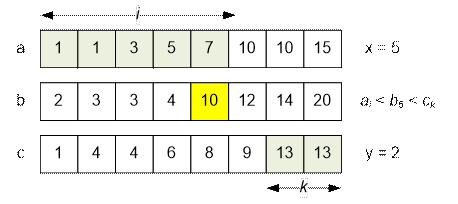
Example
Let’s consider the sorted arrays and compute
the number of valid triplets for b5 = 10.
We have: ai < b5 for i ≤ 5,
and ck > b5 for k ≥ 7.
Thus, the inequality ai < b5 < ck holds for 1 ≤ i ≤ 5 and 7 ≤ k ≤ 8.
The number of triplets (ai, b5, ck) is 5 * 2 = 10.
Algorithm implementation
Declare the arrays.
#define MAX
100000
int a[MAX], b[MAX], c[MAX];
Read the input data.
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d",
&a[i]);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d",
&b[i]);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d",
&c[i]);
Sort the arrays.
sort(a, a + n);
sort(b, b + n);
sort(c, c + n);
Count the number of valid triplets using the variable res. Iterate
over the values of bj.
res = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
The number of elements in array a
that are less than bj is x.
x =
lower_bound(a, a + n, b[j]) - a;
The number of elements in array c
that are greater than bj is y.
y = n -
(upper_bound(c, c + n, b[j]) - c);
Then, for the given value of bj, there are exactly x * y
valid triplets.
res += x *
y;
}
Print the answer.
printf("%lld\n",
res);
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int
lower_bound(int m[], int start, int end, int x)
{
while (start <
end)
{
int mid = (start + end) /
2;
if (x
<= m[mid])
end = mid;
else
start = mid + 1;
}
return start;
}
static int
upper_bound(int m[], int start, int end, int x)
{
while (start <
end)
{
int mid = (start + end) /
2;
if (x
>= m[mid])
start = mid + 1;
else
end = mid;
}
return start;
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int i, n = con.nextInt();
int a[] = new int[n];
for(i = 0;
i < n; i++) a[i] = con.nextInt();
int b[] = new int[n];
for(i = 0;
i < n; i++) b[i] = con.nextInt();
int c[] = new int[n];
for(i = 0;
i < n; i++) c[i] = con.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a); Arrays.sort(b); Arrays.sort(c);
long res = 0;
for (i = 0;
i < n; i++)
{
int x = lower_bound(a, 0, n, b[i]);
int y = n - (upper_bound(c, 0, n, b[i]));
res +=
1L * x * y;
}
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}